Difference in levels of SARS-CoV-2 S1 and S2 subunits- and nucleocapsid protein-reactive SIgM/IgM, IgG and SIgA/IgA antibodies in human milk
- PMID: 32873904
- PMCID: PMC7461757
- DOI: 10.1038/s41372-020-00805-w
Difference in levels of SARS-CoV-2 S1 and S2 subunits- and nucleocapsid protein-reactive SIgM/IgM, IgG and SIgA/IgA antibodies in human milk
Erratum in
-
Correction: Difference in levels of SARS-CoV-2 S1 and S2 subunits- and nucleocapsid protein-reactive SIgM/IgM, IgG and SIgA/IgA antibodies in human milk.J Perinatol. 2021 May;41(5):1207. doi: 10.1038/s41372-020-00816-7. J Perinatol. 2021. PMID: 32939025 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
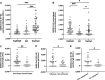
Objective: This study evaluated the presence and the levels of antibodies reactive to SARS-CoV-2 S1 and S2 subunits (S1 + S2), and nucleocapsid protein.
Study design: The levels of SARS-CoV-2 S1 + S2- and nucleocapsid-reactive SIgM/IgM, IgG and SIgA/IgA were measured in human milk samples from 41 women during the COVID-19 pandemic (2020-HM) and from 16 women 2 years prior to the outbreak (2018-HM).
Results: SARS-CoV-2 S1 + S2-reactive SIgA/IgA, SIgM/IgM and IgG were detected in 97.6%, 68.3% and 58.5% in human milk whereas nucleocapsid-reactive antibodies were detected in 56.4%, 87.2% and 46.2%, respectively. S1 + S2-reactive IgG was higher in milk from women that had symptoms of viral respiratory infection(s) during the last year than in milk from women without symptom. S1 + S2- and nucleocapsid-reactive IgG were higher in the 2020-HM group compared to the 2018-HM group.
Conclusions: The presence of SARS-CoV-2-reactive antibodies in human milk could provide passive immunity to breastfed infants and protect them against COVID-19 diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
VDM, DMD, GBM and EM are employees at Medolac Laboratories. DAS is on the scientific advisory board for Medolac Laboratories. AS and KMJ have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Human Milk Antibodies Against S1 and S2 Subunits from SARS-CoV-2, HCoV-OC43, and HCoV-229E in Mothers with A Confirmed COVID-19 PCR, Viral SYMPTOMS, and Unexposed Mothers.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 9;22(4):1749. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041749. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33572480 Free PMC article.
-
Previous viral symptoms and individual mothers influenced the leveled duration of human milk antibodies cross-reactive to S1 and S2 subunits from SARS-CoV-2, HCoV-229E, and HCoV-OC43.J Perinatol. 2021 May;41(5):952-960. doi: 10.1038/s41372-021-01001-0. Epub 2021 Mar 1. J Perinatol. 2021. PMID: 33649442 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of S1-, S2-, and NCP-Specific IgM, IgA, and IgG Antibody Kinetics in Acute SARS-CoV-2 Infection by a Microarray and Twelve Other Immunoassays.J Clin Microbiol. 2021 Apr 20;59(5):e02890-20. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02890-20. Print 2021 Apr 20. J Clin Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33602698 Free PMC article.
-
Are SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies Detectable in Human Milk After Vaccination Against COVID-19?J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2022 Apr 30;11(4):126. doi: 10.1093/jpids/piac024. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2022. PMID: 35394545 Free PMC article.
-
Titers of IgG and IgA against SARS-CoV-2 proteins and their association with symptoms in mild COVID-19 infection.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 3;14(1):12725. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-59634-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38830902 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgA and IgG in human milk after vaccination is dependent on vaccine type and previous SARS-CoV-2 exposure: a longitudinal study.Genome Med. 2022 Apr 21;14(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s13073-022-01043-9. Genome Med. 2022. PMID: 35449030 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies Detected in Mother's Milk Post-Vaccination.J Hum Lact. 2021 Aug;37(3):492-498. doi: 10.1177/08903344211030168. Epub 2021 Jul 23. J Hum Lact. 2021. PMID: 34297643 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination in Lactation: Assessment of adverse events and vaccine related antibodies in mother-infant dyads.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 Sep 16:2021.03.09.21253241. doi: 10.1101/2021.03.09.21253241. medRxiv. 2021. Update in: Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 03;12:777103. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.777103. PMID: 34373861 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Breast Milk and COVID-19: From Conventional Data to "Omics" Technologies to Investigate Changes Occurring in SARS-CoV-2 Positive Mothers.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 May 25;18(11):5668. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18115668. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34070662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 RNA and antibody detection in breast milk from a prospective multicentre study in Spain.Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2022 Mar;107(2):216-221. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2021-322463. Epub 2021 Aug 20. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2022. PMID: 34417223 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Johns Hopkins University & Medicine. COVID-19 Dashboard by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU). 2020. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

