The Effectiveness of Aromatherapy in the Management of Labor Pain and Anxiety: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 32874088
- PMCID: PMC7445940
- DOI: 10.4314/ejhs.v30i3.16
The Effectiveness of Aromatherapy in the Management of Labor Pain and Anxiety: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: Aromatherapy as an alternative and complementary medicine is a well-known method for reducing the symptoms of various physiological processes such as labor experience. The aim of this study was to systematically review the currently available evidences evaluating the use of aromatherapy for management of labor pain and anxiety.
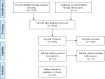
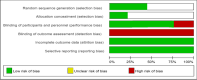
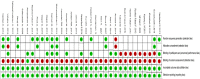
Methods: In a systematic review, 5 databases (PubMed, SCOPUS, Web of Science, Google Scholar and Scientific Information Database [SID]) were searched, from database inception up to December 2019. Keywords used included (aromatherapy OR ""essential oil" OR "aroma*") AND (pain OR anxiety) AND (labor OR delivery). Using the Cochrane Collaboration's 'Risk of bias' method; the risk of bias in the included studies was evaluated.
Results: A total of 33 studies were verified to meet our inclusion criteria. Most of the included studies were conducted in Iran. Aromatherapy was applied using inhalation, massage, footbath, birthing pool, acupressure, and compress. The most popularly used essential oil in the studies was lavender (13 studies), either as a single essential oil or in a combination with other essential oils. Most of included studies confirmed the positive effect of aromatherapy in reducing labor pain and anxiety.
Conclusion: The evidences from this study suggest that aromatherapy, as a complementary and alternative modality, can help in relieving maternal anxiety and pain during labor.
Keywords: Anxiety; Aromatherapy; Labor Pain; Systematic Review.
© 2020 Muhbubeh T., et al.
Figures
References
-
- Gholipour Baradari A, Firouzian A, Hasanzadeh Kiabi F, Emami Zeydi A, Khademloo M, Nazari Z, et al. Bolus administration of intravenous lidocaine reduces pain after an elective caesarean section: Findings from a randomised, doubleblind, placebo-controlled trial. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2017;37(5):566–570. - PubMed
-
- Lang AJ, Sorrell JT, Rodgers CS, Lebeck MM. Anxiety sensitivity as a predictor of labor pain. Eur J Pain. 2006;10(3):263–270. - PubMed
-
- Lowe NK, Corwin EJ. Proposed biological linkages between obesity, stress, and inefficient uterine contractility during labor in humans. Med Hypotheses. 2011;76(5):755. - PubMed
-
- Simkin P, Bolding A. Update on nonpharmacologic approaches to relieve labor pain and prevent suffering. J Midwifery Womens Health. 2004;49(6):489–504. - PubMed