A Literature Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis of Symptoms Prevalence in Covid-19: the Relevance of Olfactory Symptoms in Infection Not Requiring Hospitalization
- PMID: 32874091
- PMCID: PMC7453082
- DOI: 10.1007/s11940-020-00641-5
A Literature Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis of Symptoms Prevalence in Covid-19: the Relevance of Olfactory Symptoms in Infection Not Requiring Hospitalization
Abstract
Purpose of review: To investigate the association between the olfactory dysfunction and the more typical symptoms (fever, cough, dyspnoea) within the Sars-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19) in hospitalized and non-hospitalized patients.
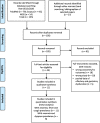
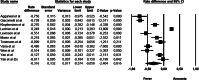
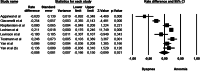
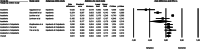
Recent findings: PubMed, Scopus and Web of Science databases were reviewed from May 5, 2020, to June 1, 2020. Inclusion criteria included English, French, German, Spanish or Italian language studies containing original data related to COVID19, anosmia, fever, cough, and dyspnoea, in both hospital and non-hospital settings. Two investigators independently reviewed all manuscripts and performed quality assessment and quantitative meta-analysis using validated tools. A third author arbitrated full-text disagreements. Following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA), 11 of 135 studies fulfilled eligibility. Anosmia was estimated less prevalent than fever and cough (respectively rate difference = - 0.316, 95% CI: - 0.574 to - 0.058, Z = - 2.404, p < 0.016, k = 11 and rate difference = - 0.249, 95% CI: - 0.402 to - 0.096, Z = - 3.185, p < 0.001, k = 11); the analysis between anosmia and dyspnoea was not significant (rate difference = - 0.008, 95% CI: - 0.166 to 0.150, Z = - 0.099, p < 0.921, k = 8). The typical symptoms were significantly more frequent than anosmia in hospitalized more critical patients than in non-hospitalized ones (respectively [Q(1) = 50.638 p < 0.000, Q(1) = 52.520 p < 0.000, Q(1) = 100.734 p < 0.000).
Summary: Patient with new onset olfactory dysfunction should be investigated for COVID-19. Anosmia is more frequent in non-hospitalized COVID-19 patients than in hospitalized ones.
Keywords: COVID-19; Hospitalization; Meta-analysis; Olfactory disorders; Sars-CoV-2.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of InterestA. Giorli declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. F. Ferretti declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. C. Biagini declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. L. Salerni declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. I. Bindi declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. S. Dasgupta declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. A. Pozza declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. G. Gualtieri declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. R. Gusinu declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. A. Coluccia declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. Marco Mandalà declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- WHO. WHO Director-General’s opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 - 11 March 2020. who.int. [Online] March 11, 2020. https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-re....
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

