Subdural empyema caused by Morganella morganii
- PMID: 32874719
- PMCID: PMC7451143
- DOI: 10.25259/SNI_136_2020
Subdural empyema caused by Morganella morganii
Abstract
Background: Morganella morganii is a species of Gram-negative enteric rod found in normal human gut flora. Pathologically, this most often presents as urinary tract infections, wound infections, and bacteremia. It is highly uncommon for M. morganii to be implicated in a central nervous system infection, with only 12 reported cases of parenchymal abscesses or meningitis.
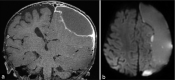
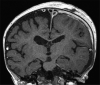
Case description: A previously healthy 13-month-old female presented with fever of unknown origin and had a witnessed seizure during evaluation. A large left subdural fluid collection was identified, and the patient underwent emergent burr hole drainage and subdural drain placement. Cultures demonstrated M. morganii empyema, and she subsequently completed a course of directed antibiotics. Six months following surgery, she has no further clinical or radiographic evidence of infection, seizures, or neurological sequelae.
Conclusion: We describe the first reported case of isolated subdural empyema caused by M. morganii. The child was successfully treated with the evacuation of the empyema and direct antibiotics with no lasting neurological injury.
Keywords: Infection; Morganella morganii; Pediatric neurosurgery; Subdural empyema.
Copyright: © 2020 Surgical Neurology International.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abdalla J, Saad M, Samnani I, Lee P, Moorman J. Central nervous system infection caused by Morganella morganii. Am J Med Sci. 2006;331:44–7. - PubMed
-
- Águeda S, Leitão A, Rocha G, Guimarães H. Cerebral abscess and empyema due to Morganella morganii. Pediatr Ther. 2013;3:147.
-
- Gupta S, Vachhrajani S, Kulkarni AV, Taylor MD, Dirks P, Drake JM, et al. Neurosurgical management of extraaxial central nervous system infections in children. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2011;7:441–51. - PubMed
-
- Jim KK, Brouwer MC, van der Ende A, van de Beek D. Subdural empyema in bacterial meningitis. Neurology. 2012;79:2133–9. - PubMed
-
- Konar S, Gohil D, Shukla D, Sadashiva N, Uppar A, Bhat DI, et al. Predictors of outcome of subdural empyema in children. Neurosurg Focus. 2019;47:E17. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
