Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Causing Empyema Necessitans and Pyomyositis in an Immunocompetent Patient
- PMID: 32874788
- PMCID: PMC7455391
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.9454
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Causing Empyema Necessitans and Pyomyositis in an Immunocompetent Patient
Abstract
Empyema necessitans is a relatively rare clinical entity in which the empyema extends through the parietal pleura into the adjacent soft tissue and musculature of the chest wall. It usually occurs due to inadequate treatment of a primary lung infection. Aggregatibacter (formerly Actinobacillus) actinomycetemcomitans is a facultative anaerobic gram-negative coccobacillus that is part of the normal oral flora. Infections due to this organism usually result from aspiration in conjunction with dental disease or trauma to the oral mucosa resulting in pneumonia or empyema. It often coinfects with Actinomyces and is known to cause empyema necessitans. Cases of monomicrobial empyema necessitans due to Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans in adults have rarely been reported with four such publications found on review of the literature. We present a patient with severe periodontitis who developed empyema necessitans due to Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans likely from aspiration complicated by pyomyositis of the right triceps brachii and a left posterior thigh abscess.
Keywords: aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans; empyema necessitans; empyema necessitatis; immunocompetent; pyomyositis.
Copyright © 2020, Homsi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
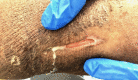

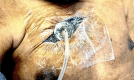
Similar articles
-
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans infection in a 15-year-old boy with pulmonary empyema: a case report and review of literature.Ital J Pediatr. 2023 Mar 31;49(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s13052-023-01429-4. Ital J Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37004059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mixed Actinomyces israelii and Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans infection causing empyema necessitatis and multiple skin abscesses in an immunocompetent patient.BMJ Case Rep. 2019 Sep 24;12(9):e230287. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2019-230287. BMJ Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 31551318 Free PMC article.
-
Subcutaneous abscess due to empyema necessitans caused by Porphyromonas gingivalis in a patient with periodontitis.IDCases. 2022 Feb 21;27:e01458. doi: 10.1016/j.idcr.2022.e01458. eCollection 2022. IDCases. 2022. PMID: 35242562 Free PMC article.
-
A Complicated Case of Group B Streptococcus Empyema Necessitans.Cureus. 2017 Aug 22;9(8):e1591. doi: 10.7759/cureus.1591. Cureus. 2017. PMID: 29062623 Free PMC article.
-
Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans pneumonia with chest wall involvement and rib destruction.Chest. 1992 May;101(5):1450-2. doi: 10.1378/chest.101.5.1450. Chest. 1992. PMID: 1582318 Review.
Cited by
-
Empyema necessitans mimicking mesothelioma; unusual presentation of active pulmonary TB in immuno-competent state.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022 Mar 3;75:103464. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.103464. eCollection 2022 Mar. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022. PMID: 35386768 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous Rupture of Empyema Necessitans in the Emergency Department.Cureus. 2021 May 3;13(5):e14822. doi: 10.7759/cureus.14822. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34094776 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the relationship between periodontopathogens and respiratory diseases (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2024 Mar;29(3):42. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13166. Epub 2024 Jan 19. Mol Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 38240101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Empyema Necessitatis Caused by Prevotella melaninogenica and Dialister pneumosintes Resolved with Vacuum-Assisted Closure System: A Case Report.Microorganisms. 2024 Sep 12;12(9):1881. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12091881. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39338554 Free PMC article.
-
Comments and Illustrations of the European Federation of Societies for Ultrasound in Medicine Guidelines: Benign Pleura Lesions (Benign Pleura Thickening, Lesions and Masses)-What Can Be Seen on Transthoracic Ultrasound?Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jan 14;15(2):176. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15020176. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39857060 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tuberculous empyema necessitates. Porcel JM, Madroñero AB, Bielsa S. Respiration. 2004;71:191. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
