Impacts and challenges of United States medical students during the COVID-19 pandemic
- PMID: 32874968
- PMCID: PMC7441247
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i15.3136
Impacts and challenges of United States medical students during the COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract
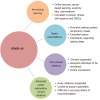
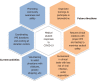
The delivery of medical student education has changed rapidly during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. Students in their pre-clinical years have transitioned to online courses and examinations. Students in their clinical years are not permitted on clinical rotations, and face uncertainties in career exploration and the residency application process. Medical students in all stages of training are volunteering and helping their communities. The future presence of COVID-19 throughout the United States is unknown, and medical students are eager to return to their training. This paper outlines current challenges in medical student education and the various responses that have been adopted. We also discuss possible future directions for students through involvement in telemedicine, outpatient clinic visits, and non-respiratory inpatient care tasks as adequate personal protective equipment, COVID-19 testing, and resources become more widely available.
Keywords: COVID-19; Education; Healthcare delivery; Medical students; Schools; Telemedicine.
©The Author(s) 2020. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

