Blended Learning Is a Feasible and Effective Tool for Basic Pediatric Spinal Deformity Training
- PMID: 32875908
- PMCID: PMC7882832
- DOI: 10.1177/2192568220916502
Blended Learning Is a Feasible and Effective Tool for Basic Pediatric Spinal Deformity Training
Abstract
Study design: Descriptive study.
Objective: Assessing the applicability of blended learning to specific domains of spine surgery.
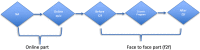
Methods: After the needs assessment, a blended pediatric spine deformity course program was designed. A total of 33 participants, including orthopedic and neurosurgeons, registered for the course and all of them completed an online entrance quiz. Thus, they were eligible to have online part of course, which included the theoretical part of the course and also a discussion forum where the discussions about the topics facilitated by faculty. Thirteen of 33 subjects participated second part of the blended pediatric spine deformity course. This face-to-face (F2F) part consisted of case discussions for each topic and discussions facilitated by faculty members. The same quiz was also taken before and after the F2F part. All quiz results were compared statistically.
Results: There were 11 lectures within the online part and 6 case discussions in the F2F part. The quiz scores were improved significantly by having a complete blended pediatric deformity course (P < .05).
Conclusions: The current study has demonstrated that blended learning format, including online and F2F, is feasible and effective in training for a domain of spine surgery, pediatric deformity in this specific context.
Keywords: blended learning; e-learning; postgraduate education; spine surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Efficacy of Blended Learning in a Pediatric Spine Deformity Management Program in Sub-Saharan Africa.J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2023 Feb 3;7(2):e22.00128. doi: 10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-22-00128. eCollection 2023 Feb 1. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2023. PMID: 36745534 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Blended Online Learning in Three Spinal Surgery Educational Courses.J Eur CME. 2022 Feb 9;11(1):2014042. doi: 10.1080/21614083.2021.2014042. eCollection 2022. J Eur CME. 2022. PMID: 35173996 Free PMC article.
-
Intrinsic motivation between face-to-face and blended learning in surgical clinical education.Pak J Med Sci. 2024 May-Jun;40(5):913-917. doi: 10.12669/pjms.40.5.1048. Pak J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38827872 Free PMC article.
-
Health worker text messaging for blended learning, peer support, and mentoring in pediatric and adolescent HIV/AIDS care: a case study in Zimbabwe.Hum Resour Health. 2019 Jun 7;17(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s12960-019-0364-6. Hum Resour Health. 2019. PMID: 31174543 Free PMC article.
-
Blended and e-learning in pediatric education: harnessing lessons learned from the COVID-19 pandemic.Eur J Pediatr. 2022 Feb;181(2):447-452. doi: 10.1007/s00431-021-04149-1. Epub 2021 Jul 29. Eur J Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 34322730 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development and evaluation of an efficient training program to facilitate the adoption of a novel neurorehabilitation device.J Rehabil Assist Technol Eng. 2023 Feb 14;10:20556683231158552. doi: 10.1177/20556683231158552. eCollection 2023 Jan-Dec. J Rehabil Assist Technol Eng. 2023. PMID: 36818163 Free PMC article.
-
The Efficacy of Blended Learning in a Pediatric Spine Deformity Management Program in Sub-Saharan Africa.J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2023 Feb 3;7(2):e22.00128. doi: 10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-22-00128. eCollection 2023 Feb 1. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2023. PMID: 36745534 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Blended Online Learning in Three Spinal Surgery Educational Courses.J Eur CME. 2022 Feb 9;11(1):2014042. doi: 10.1080/21614083.2021.2014042. eCollection 2022. J Eur CME. 2022. PMID: 35173996 Free PMC article.
-
Team-Based Learning and Lecture-Based Learning: Comparison of Sudanese Medical Students' Performance.Adv Med Educ Pract. 2021 Dec 24;12:1513-1519. doi: 10.2147/AMEP.S331296. eCollection 2021. Adv Med Educ Pract. 2021. PMID: 34992488 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of a Flipped Classroom Didactic Curriculum on Orthopaedic In-Training Examination Scores for a Resident Cohort.JB JS Open Access. 2024 Oct 30;9(4):e24.00107. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.OA.24.00107. eCollection 2024 Oct-Dec. JB JS Open Access. 2024. PMID: 39479403 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Keifenheim KE, Velten-Schurian K, Fahse B, et al. “A change would do you good”: training medical students in Motivational Interviewing using a blended-learning approach—a pilot evaluation. Patient Educ Couns. 2019;102:663–669. - PubMed
-
- Rowe M, Frantz J, Bozalek V. The role of blended learning in the clinical education of healthcare students: a systematic review. Med Teach. 2012;34:e216–e221. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources