Clinicopathological and Prognostic Significance of the EML4-ALK Translocation and IGFR1, TTF1, Napsin A Expression in Patients with Lung Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 32876329
- PMCID: PMC10508933
- DOI: 10.5146/tjpath.2020.01503
Clinicopathological and Prognostic Significance of the EML4-ALK Translocation and IGFR1, TTF1, Napsin A Expression in Patients with Lung Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Objective: Patients with lung adenocarcinoma who harbor ALK gene rearrangements can demonstrate significant clinical benefit with ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGFR1) is a cellular membrane receptor that is overexpressed in many tumors. It plays an important role in cancer progression and is associated with increased postoperative recurrence and poorer disease-free survival. The aim of this study was to determine the EML4-ALK mutation and IGFR1 expression in lung adenocarcinoma and analyze their prognostic value.
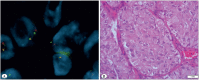
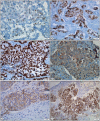
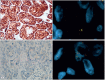
Material and method: In this study, we analyzed the EML4-ALK mutation using the FISH and IHC techniques in 251 lung adenocarcinoma (203 primary resections, 48 metastasectomies) cases. Correlative analyses were performed between the EML4-ALK mutation, the IGFR1, TTF1, and NapsinA expression, and the clinicopathologic factors in lung adenocarcinomas.
Results: The EML4-ALK mutation was observed in 3.8% of the cases and it was associated with the solid pattern, signet ring cell morphology, and larger tumor size. IGFR1 expression was identified in 49% of the cases and most of the ALK-mutated cases were also expressing the IGFR1 protein (66%). IGFR1 expression frequency was increased in metastasectomy specimens.
Conclusion: A solid signet-ring cell pattern or mucinous cribriform pattern was present at least focally in all ALK-positive tumors, consistently with the literature. In addition, IGFR1 expression levels showed an increase in the EML4-ALK-mutated cases in our series, but the clinical significance of this finding should be supported by larger series and survival analysis. Our findings show that IGFR1 expression may be useful as a poor prognostic marker in patients with lung adenocarcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no confict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
EML4-ALK translocation predicts better outcome in lung adenocarcinoma patients with wild-type EGFR.J Thorac Oncol. 2012 Jan;7(1):98-104. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3182370e30. J Thorac Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22124476
-
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase translocation is correlated with anaplastic lymphoma kinase expression and mutually exclusive with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation in Taiwanese non-small cell lung cancer.Pathol Int. 2015 May;65(5):231-9. doi: 10.1111/pin.12268. Epub 2015 Feb 23. Pathol Int. 2015. PMID: 25708242
-
Clinical features and outcome of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer who harbor EML4-ALK.J Clin Oncol. 2009 Sep 10;27(26):4247-53. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.22.6993. Epub 2009 Aug 10. J Clin Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19667264 Free PMC article.
-
Colorectal Adenocarcinomas Harboring ALK Fusion Genes: A Clinicopathologic and Molecular Genetic Study of 12 Cases and Review of the Literature.Am J Surg Pathol. 2020 Sep;44(9):1224-1234. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000001512. Am J Surg Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32804454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atypical Histopathological Aspects of Common Types of Lung Cancer-Our Experience and Literature Review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Jan 7;60(1):112. doi: 10.3390/medicina60010112. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38256374 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of alectinib in lung adenocarcinoma patients with different anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) rearrangements and co-existing alterations-a retrospective cohort study.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2023 Dec 26;12(12):2505-2519. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-23-658. Epub 2023 Nov 22. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 38205204 Free PMC article.
-
Napsin A Expression in Human Tumors and Normal Tissues.Pathol Oncol Res. 2021 Apr 20;27:613099. doi: 10.3389/pore.2021.613099. eCollection 2021. Pathol Oncol Res. 2021. PMID: 34257582 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated lung adenocarcinoma diagnosed from endometrial polyp metastasis: A case report and literature review.Turk J Obstet Gynecol. 2022 Mar 28;19(1):81-86. doi: 10.4274/tjod.galenos.2021.58046. Turk J Obstet Gynecol. 2022. PMID: 35343222 Free PMC article.
-
A Japanese case of ovarian mucinous adenocarcinoma with germline double variants of MSH2 and BRCA2.J Hum Genet. 2023 Nov;68(11):783-787. doi: 10.1038/s10038-023-01178-6. Epub 2023 Jul 7. J Hum Genet. 2023. PMID: 37420004
-
Diagnostic gastrointestinal markers in primary lung cancer and pulmonary metastases.Virchows Arch. 2024 Aug;485(2):347-357. doi: 10.1007/s00428-023-03583-w. Epub 2023 Jun 22. Virchows Arch. 2024. PMID: 37349623 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Isaka Tetsuya, Nakayama Haruhiko, Ito Hiroyuki, Yokose Tomoyuki, Yamada Kouzo, Masuda Munetaka. Impact of the epidermal growth factor receptor mutation status on the prognosis of recurrent adenocarcinoma of the lung after curative surgery. Oct;2018 BMC Cancer. 18:959–959. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4849-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Soda Manabu, Choi Young Lim, Enomoto Munehiro, Takada Shuji, Yamashita Yoshihiro, Ishikawa Shunpei, Fujiwara Shin-ichiro, Watanabe Hideki, Kurashina Kentaro, Hatanaka Hisashi, Bando Masashi, Ohno Shoji, Ishikawa Yuichi, Aburatani Hiroyuki, Niki Toshiro, Sohara Yasunori, Sugiyama Yukihiko, Mano Hiroyuki. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Aug;2007 Nature. 448:561–566. doi: 10.1038/nature05945. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

