Evidence for possible association of vitamin D status with cytokine storm and unregulated inflammation in COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 32876941
- PMCID: PMC7465887
- DOI: 10.1007/s40520-020-01677-y
Evidence for possible association of vitamin D status with cytokine storm and unregulated inflammation in COVID-19 patients
Erratum in
-
Correction: Evidence for possible association of vitamin D status with cytokine storm and unregulated inflammation in COVID-19 patients.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2023 Dec;35(12):3263. doi: 10.1007/s40520-023-02627-0. Epub 2023 Dec 8. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2023. PMID: 38064110 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objectives: We present evidence for a possible role of Vitamin D (VitD) deficiency in unregulated cytokine production and inflammation leading to complications in COVID-19 patients.
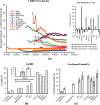
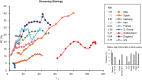
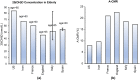
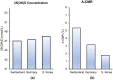
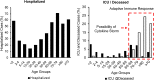
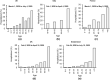
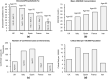
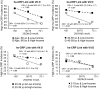
Design: The time-adjusted case mortality ratio (T-CMR) was estimated as the ratio of deceased patients on day N to the confirmed cases on day N-8. The adaptive average of T-CMR (A-CMR) was calculated as a metric of COVID-19 associated mortality. A model based on positivity change (PC) and an estimated prevalence of COVID-19 was used to determine countries with similar screening strategies. A possible association of A-CMR with the mean concentration of 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) in elderly individuals in countries with similar screening strategy was investigated. We considered high C-reactive protein (CRP) in severe COVID-19 patients (CRP ≥ 1 mg/dL) as a surrogate of a cytokine storm. We considered high-sensitivity CRP (hs-CRP) in healthy subjects as hs-CRP ≥ 0.2 mg/dL.
Results: A link between 25(OH)D and A-CMR in countries with similar screening strategy is evidence for VitD's possible role in reducing unregulated cytokine production and inflammation among patients with severe COVID-19. We observed an odds ratio (OR) of 1.8 with 95% confidence interval (95% CI) (1.2 to 2.6) and an OR of 1.9 with 95% CI (1.4 to 2.7) for hs-CRP in VitD deficient elderly from low-income families and high-income families, respectively. COVID-19 patient-level data show an OR of 3.4 with 95% CI (2.15 to 5.4) for high CRP in severe COVID-19 patients.
Conclusion: We conclude that future studies on VitD's role in reducing cytokine storm and COVID-19 mortality are warranted.
Keywords: C-reactive protein; COVID-19; Case mortality ratio; Cytokine storm; SARS-CoV-2; Vitamin D.
Conflict of interest statement
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures



Comment in
-
Vitamin D status and COVID-19 in older adults.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2020 Nov;32(11):2425-2426. doi: 10.1007/s40520-020-01716-8. Epub 2020 Sep 21. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2020. PMID: 32955676 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Yao H, Lu X, Chen Q, et al. Patient-derived mutations impact pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2. medRxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.04.14.20060160. - DOI
-
- Coronavirus has mutated into 30 strains and ones in US are less deadlier than those in Europe, finds study. In: News Break. https://www.newsbreak.com/news/0OoSRJjb/coronavirus-has-mutated-into-30-.... Accessed 21 Apr 2020
-
- Kanchan T, Kumar N, Unnikrishnan B. Encyclopedia of forensic and legal medicine. Amsterdam: Elsevier Inc.; 2015. Mortality: statistics; pp. 572–577.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

