Prospective Evaluation of PI-RADS Version 2.1 for Prostate Cancer Detection
- PMID: 32877244
- PMCID: PMC8974984
- DOI: 10.2214/AJR.19.22679
Prospective Evaluation of PI-RADS Version 2.1 for Prostate Cancer Detection
Abstract
OBJECTIVE. The purpose of this study was to prospectively evaluate Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data and System version 2.1 (PI-RADSv2.1), which was released in March 2019 to update version 2.0, for prostate cancer detection with transrectal ultrasound-MRI fusion biopsy and 12-core systematic biopsy. SUBJECTS AND METHODS. This prospective study included 110 consecutively registered patients who underwent multiparametric MRI evaluated with PI-RADSv2.1 criteria followed by fusion biopsy and systematic biopsy between April and September 2019. Lesion-based cancer detection rates (CDRs) were calculated for prostate cancer (Gleason grade group, > 0) and clinically significant prostate cancer (Gleason grade group, > 1). RESULTS. A total of 171 lesions (median size, 1.1 cm) in 110 patients were detected and evaluated with PI-RADSv2.1. In 16 patients no lesion was detected, and only systematic biopsy was performed. Lesions were categorized as follows: PI-RADS category 1, 1 lesion; PI-RADS category 2, 34 lesions; PI-RADS category 3, 54 lesions; PI-RADS category 4, 52 lesions; and PI-RADS category 5, 30 lesions. Histopathologic analysis revealed prostate cancer in 74 of 171 (43.3%) lesions and clinically significant prostate cancer in 57 of 171 (33.3%) lesions. The CDRs of prostate cancer for PI-RADS 2, 3, 4, and 5 lesions were 20.0%, 24.1%, 51.9%, and 90.0%. The CDRs of clinically significant prostate cancer for PI-RADS 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 lesions were 0%, 5.7%, 14.8%, 44.2%, and 80.0%. In 16 patients with normal multiparametric MRI findings (PI-RADS 1), the CDRs were 50.0% for PCa and 18.8% for clinically significant prostate cancer. CONCLUSION. This investigation yielded CDRs assessed with prospectively assigned PI-RADSv2.1 scores. CDRs increased with higher PI-RADSv2.1 scores. These results can be compared with previously published outcomes derived with PI-RADS version 2.0.
Keywords: PI-RADS; early detection; multiparametric MRI; prostate biopsy; prostate cancer.
Figures

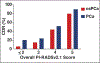
Comment in
-
Imaging.J Urol. 2021 Apr;205(4):1205-1206. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000001619. Epub 2021 Jan 19. J Urol. 2021. PMID: 33464932 No abstract available.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin 2019; 69:7–34 - PubMed
-
- Noguchi M, Stamey TA, McNeal JE, Yemoto CM. Relationship between systematic biopsies and histological features of 222 radical prostatectomy specimens: lack of prediction of tumor significance for men with nonpalpable prostate cancer. J Urol 2001; 166:104–109; discussion, 109–110 - PubMed
-
- de Rooij M, Hamoen EHJ, Fütterer JJ, Barentsz JO, Rovers MM. Accuracy of multiparametric MRI for prostate cancer detection: a meta-analysis. AJR 2014; 202:343–351 - PubMed
-
- Ahmed HU, El-Shater Bosaily A, Brown LC, et al.; PROMIS study group. Diagnostic accuracy of multi-parametric MRI and TRUS biopsy in prostate cancer (PROMIS): a paired validating confirmatorystudy.Lancet 2017; 389:815–822. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

