Cell Cycle Checkpoints Cooperate to Suppress DNA- and RNA-Associated Molecular Pattern Recognition and Anti-Tumor Immune Responses
- PMID: 32877684
- PMCID: PMC7530826
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108080
Cell Cycle Checkpoints Cooperate to Suppress DNA- and RNA-Associated Molecular Pattern Recognition and Anti-Tumor Immune Responses
Abstract
The DNA-dependent pattern recognition receptor, cGAS (cyclic GMP-AMP synthase), mediates communication between the DNA damage and the immune responses. Mitotic chromosome missegregation stimulates cGAS activity; however, it is unclear whether progression through mitosis is required for cancercell-intrinsic activation of anti-tumor immune responses. Moreover, it is unknown whether cell cycle checkpoint disruption can restore responses in cancer cells that are recalcitrant to DNAdamage-induced inflammation. Here, we demonstrate that prolonged cell cycle arrest at the G2-mitosis boundary from either excessive DNA damage or CDK1 inhibition prevents inflammatory-stimulated gene expression and immune-mediated destruction of distal tumors. Remarkably, DNAdamage-induced inflammatory signaling is restored in a RIG-I-dependent manner upon concomitant disruption of p53 and the G2 checkpoint. These findings link aberrant cell progression and p53 loss to an expanded spectrum of damage-associated molecular pattern recognition and have implications for the design of rational approaches to augment anti-tumor immune responses.
Keywords: ATR; DNA damage; RIG-I; anti-tumor immune response; cGAS; cell cycle checkpoint; inflammatory signaling; p53.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
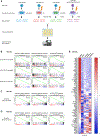

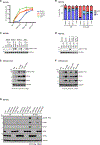
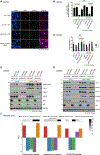
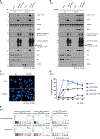
References
-
- Ablasser A, and Hur S. (2020). Regulation of cGAS- and RLR-mediated immunity to nucleic acids. Nat. Immunol. 21, 17–29. - PubMed
-
- Abraham RT (2001). Cell cycle checkpoint signaling through the ATM and ATR kinases. Genes Dev. 15, 2177–2196. - PubMed
-
- Barlow C, Brown KD, Deng CX, Tagle DA, and Wynshaw-Boris A. (1997). Atm selectively regulates distinct p53-dependent cell-cycle checkpoint and apoptotic pathways. Nat. Genet. 17, 453–456. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

