Biological basis of bone strength: anatomy, physiology and measurement
- PMID: 32877972
- PMCID: PMC7493450
Biological basis of bone strength: anatomy, physiology and measurement
Abstract
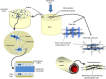
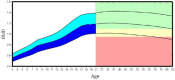
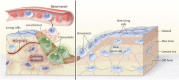
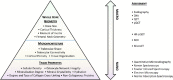
Understanding how bones are innately designed, robustly developed and delicately maintained through intricate anatomical features and physiological processes across the lifespan is vital to inform our assessment of normal bone health, and essential to aid our interpretation of adverse clinical outcomes affecting bone through primary or secondary causes. Accordingly this review serves to introduce new researchers and clinicians engaging with bone and mineral metabolism, and provide a contemporary update for established researchers or clinicians. Specifically, we describe the mechanical and non-mechanical functions of the skeleton; its multidimensional and hierarchical anatomy (macroscopic, microscopic, organic, inorganic, woven and lamellar features); its cellular and hormonal physiology (deterministic and homeostatic processes that govern and regulate bone); and processes of mechanotransduction, modelling, remodelling and degradation that underpin bone adaptation or maladaptation. In addition, we also explore commonly used methods for measuring bone metabolic activity or material features (imaging or biochemical markers) together with their limitations.
Keywords: Cortical; Imaging; Modelling; Remodelling; Trabecular.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fonseca H, Moreira-Gonçalves D, Coriolano H-JA, Duarte JA. Bone quality:The determinants of bone strength and fragility. Sports Med. 2014;44(1):37–53. - PubMed
-
- Cardinale M, Newton R, Nosaka K. Portland, OR: John Wiley &Sons; 2011. Strength and conditioning:Biological principles and practical applications.
-
- Ritchie RO, Buehler MJ, Hansma P. Plasticity and toughness in bone. Phys Today. 2009;62(6):41–7.
-
- Korhonen MT, Heinonen A, Siekkinen J, Isolehto J, Alén M, Kiviranta I, et al. Bone density, structure and strength, and their determinants in aging sprint athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2012;44(12):2340–9. - PubMed
