Effects of IL-6 Signaling Pathway Inhibition on Weight and BMI: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 32878032
- PMCID: PMC7504579
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21176290
Effects of IL-6 Signaling Pathway Inhibition on Weight and BMI: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
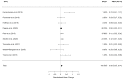
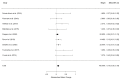
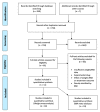
Inhibitors of the IL-6 signaling pathway, such as tocilizumab, are frequently administered for the treatment of immune diseases, e.g., rheumatoid arthritis and multicentric Castleman's disease. The aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to ascertain the effects of IL-6 pathway inhibitors on weight and body mass index (BMI). Using PRISMA guidelines, we systematically reviewed relevant articles from three databases (PubMed, OVID, EMBASE). A random effects model was used to estimate standardized mean change (SMCC). Ten studies with a total of 1531 patients were included in the meta-analysis for weight and ten studies with a total of 1537 patients were included in the BMI meta-analysis. The most commonly administered IL-6 pathway inhibitor was tocilizumab. IL-6 pathway inhibitors were associated with increases in weight (SMCC = 0.09, p = 0.016, 95% CI [0.03, 0.14]) and BMI (SMCC = 0.10, p = 0.0001, 95% CI [0.05, 0.15]). These findings suggest that the IL-6 pathway is involved in weight regulation. Modulating IL-6 signaling may be a potential future therapeutic avenue used as an adjunct for the treatment of disorders associated with weight changes, such as cancer cachexia and anorexia nervosa.
Keywords: BMI; IL-6; obesity; rheumatoid arthritis; siltuximab; spondyloarthritis; tocilizumab; weight.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dubiński A., Zdrojewicz Z. The role of interleukin-6 in development and progression of atherosclerosis. Polski Merkur. Lek. Organ Polskiego Towar. Lek. 2007;22:291–294. - PubMed
-
- Schoels M.M., Van Der Heijde D., Breedveld F.C., Burmester G.R., Dougados M., Emery P., Ferraccioli G., Gabay C., Gibofsky A., Gomez-Reino J.J., et al. Blocking the effects of interleukin-6 in rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory rheumatic diseases: Systematic literature review and meta-analysis informing a consensus statement. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012;72:583–589. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202470. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

