Green Synthesis of Ni@PEDOT and Ni@PEDOT/Au (Core@Shell) Inverse Opals for Simultaneous Detection of Ascorbic Acid, Dopamine, and Uric Acid
- PMID: 32878039
- PMCID: PMC7558593
- DOI: 10.3390/nano10091722
Green Synthesis of Ni@PEDOT and Ni@PEDOT/Au (Core@Shell) Inverse Opals for Simultaneous Detection of Ascorbic Acid, Dopamine, and Uric Acid
Abstract
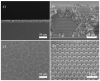
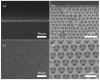
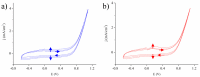
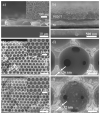
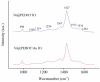
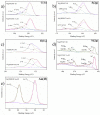
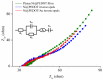
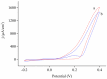
We demonstrate a water-based synthetic route to fabricate composite inverse opals for simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid (AA), dopamine (DA), and uric acid (UA). Our process involves the conformal deposition of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) and PEDOT/Au on the skeletons of Ni inverse opals via cyclic voltammetric scans (CV) to initiate the electropolymerization of 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene (EDOT) monomers. The resulting samples, Ni@PEDOT, and Ni@PEDOT/Au inverse opals, exhibit a three-dimensional ordered macroporous platform with a large surface area and interconnected pore channels, desirable attributes for facile mass transfer and strong reaction for analytes. Structural characterization and material/chemical analysis including scanning electron microscope, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and Raman spectroscopy are carried out. The sensing performances of Ni@PEDOT and Ni@PEDOT/Au inverse opals are explored by conducting CV scans with various concentrations of AA, DA, and UA. By leveraging the structural advantages of inverse opals and the selection of PEDOT/Au composite, the Ni@PEDOT/Au inverse opals reveal improved sensing performances over those of conventional PEDOT-based nanostructured sensors.
Keywords: Au nanoparticles; PEDOT; ascorbic acid; colloidal crystals; dopamine; electrochemical sensing; inverse opals; uric acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Chew B.P. Antioxidant vitamins affect food animal immunity and health. J. Nutr. 1995;125:1804S–1808S. - PubMed
-
- Faure H., Preziosi P., Roussel A., Bertrais S., Galan P., Hercberg S., Favier A. Factors influencing blood concentration of retinol, alpha-tocopherol, vitamin C, and beta-carotene in the French participants of the SU.VI.MAX trial. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006;60:706–717. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602372. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

