Educational Interventions for Teaching Evidence-Based Practice to Undergraduate Nursing Students: A Scoping Review
- PMID: 32878256
- PMCID: PMC7503534
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17176351
Educational Interventions for Teaching Evidence-Based Practice to Undergraduate Nursing Students: A Scoping Review
Abstract
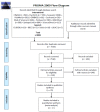
Background: Evidence-based practice (EBP) is the appropriate approach to guide healthcare personnel in their clinical practice. Despite the importance of EBP, undergraduate nursing students are not very much engaged and have a lack of knowledge and skills. Aim: The aim of this study was to gather, assess and synthesize evidence on educational interventions promoting evidence-based practice competencies in traditional undergraduate nursing students. Methods: This is a scoping review on sixteen English and non-English databases. A data extraction form was established including authors, year of publication, country, types of participant, specific objectives, study design, educational intervention, comparison if existed, and outcomes of significance. Results: The search strategy retrieved 8901 records in total. After screening for duplicates and eligibility, 20 articles were included in the qualitative synthesis. Improvement in EBP domains such as knowledge, skills, attitudes/behaviours, EBP beliefs, use, practice, level of evidence, critical thinking and future use of EBP were mentioned and assessed in different studies. Conclusions: EBP training can improve nursing students' capacity in healthcare provision. Teaching EBP competencies along undergraduate nursing curricula should be a high priority at nursing programmes. The use of innovative approaches seems to be more effective than traditional ways. Education of EBP increases its future use and critical thinking and EBP programs improve self-efficacy and the level of evidence utilization.
Keywords: evidence-based nursing; evidence-based practice; nursing education; nursing students; teaching EBP; undergraduate students.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Straus S.E., Glasziou P., Richardson W.S., Haynes R.B. Evidence-Based Medicine E-Book: How to Practice and Teach EBM. Elsevier Health Sciences; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2018.
-
- American Nurses Association . Nursing Scope and Standards of Practice. 3rd ed. Silver Spring; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2015.
-
- European Federation of Nurses Associations . EFN Competency Framework. EFN Guideline to Implement Article 31 into National Nurses’ Education Programmes. European Federation of Nurses Associations; Brussels, Belgium: 2015.
-
- Institute of Medicine . The Future of Nursing: Leading Change, Advancing Health. National Academies Press; Washington, DC, USA: 2010. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

