Expansion of SARS-CoV-2-Specific Antibody-Secreting Cells and Generation of Neutralizing Antibodies in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients
- PMID: 32878912
- PMCID: PMC7576114
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.2000717
Expansion of SARS-CoV-2-Specific Antibody-Secreting Cells and Generation of Neutralizing Antibodies in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients
Abstract
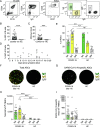
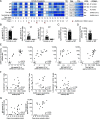
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), emerged in late 2019 and has since become a global pandemic. Pathogen-specific Abs are typically a major predictor of protective immunity, yet human B cell and Ab responses during COVID-19 are not fully understood. In this study, we analyzed Ab-secreting cell and Ab responses in 20 hospitalized COVID-19 patients. The patients exhibited typical symptoms of COVID-19 and presented with reduced lymphocyte numbers and increased T cell and B cell activation. Importantly, we detected an expansion of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein-specific Ab-secreting cells in all 20 COVID-19 patients using a multicolor FluoroSpot Assay. Out of the 20 patients, 16 had developed SARS-CoV-2-neutralizing Abs by the time of inclusion in the study. SARS-CoV-2-specific IgA, IgG, and IgM Ab levels positively correlated with SARS-CoV-2-neutralizing Ab titers, suggesting that SARS-CoV-2-specific Ab levels may reflect the titers of neutralizing Abs in COVID-19 patients during the acute phase of infection. Last, we showed that IL-6 and C-reactive protein serum concentrations were higher in patients who were hospitalized for longer, supporting the recent observations that IL-6 and C-reactive protein could be used as markers for COVID-19 severity. Altogether, this study constitutes a detailed description of clinical and immunological parameters in 20 COVID-19 patients, with a focus on B cell and Ab responses, and describes tools to study immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination.
Copyright © 2020 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Nutt S. L., Hodgkin P. D., Tarlinton D. M., Corcoran L. M. 2015. The generation of antibody-secreting plasma cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 15: 160–171. - PubMed
-
- Huang K.-Y. A., Li C. K.-F., Clutterbuck E., Chui C., Wilkinson T., Gilbert A., Oxford J., Lambkin-Williams R., Lin T.-Y., McMichael A. J., Xu X.-N. 2014. Virus-specific antibody secreting cell, memory B-cell, and sero-antibody responses in the human influenza challenge model. J. Infect. Dis. 209: 1354–1361. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

