Violet-light suppression of thermogenesis by opsin 5 hypothalamic neurons
- PMID: 32879486
- PMCID: PMC8130195
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2683-0
Violet-light suppression of thermogenesis by opsin 5 hypothalamic neurons
Abstract
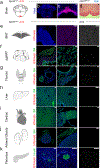
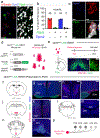
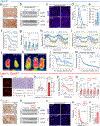
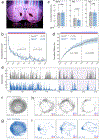
The opsin family of G-protein-coupled receptors are used as light detectors in animals. Opsin 5 (also known as neuropsin or OPN5) is a highly conserved opsin that is sensitive to visible violet light1,2. In mice, OPN5 is a known photoreceptor in the retina3 and skin4 but is also expressed in the hypothalamic preoptic area (POA)5. Here we describe a light-sensing pathway in which POA neurons that express Opn5 regulate thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue (BAT). We show that Opn5 is expressed in glutamatergic warm-sensing POA neurons that receive synaptic input from several thermoregulatory nuclei. We further show that Opn5 POA neurons project to BAT and decrease its activity under chemogenetic stimulation. Opn5-null mice show overactive BAT, increased body temperature, and exaggerated thermogenesis when cold-challenged. Moreover, violet photostimulation during cold exposure acutely suppresses BAT temperature in wild-type mice but not in Opn5-null mice. Direct measurements of intracellular cAMP ex vivo show that Opn5 POA neurons increase cAMP when stimulated with violet light. This analysis thus identifies a violet light-sensitive deep brain photoreceptor that normally suppresses BAT thermogenesis.
Figures









Comment in
-
Light-activated neurons deep in the brain control body heat.Nature. 2020 Sep;585(7825):351-352. doi: 10.1038/d41586-020-02481-4. Nature. 2020. PMID: 32879476 No abstract available.
-
Light-sensing at depth.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2020 Nov;21(11):591. doi: 10.1038/s41583-020-00391-y. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32999469 No abstract available.
References
-
- Tarttelin EE, Bellingham J, Hankins MW, Foster RG & Lucas RJ Neuropsin (Opn5): A novel opsin identified in mammalian neural tissue. FEBS Lett. 554, 410–416 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

