Is vitamin D status reflected by testosterone concentration in elite athletes?
- PMID: 32879544
- PMCID: PMC7433328
- DOI: 10.5114/biolsport.2020.95633
Is vitamin D status reflected by testosterone concentration in elite athletes?
Abstract
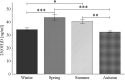
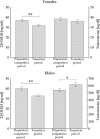
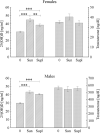
Vitamin D is a nutrient whose active form affects tissues as a hormone and possibly enhances performance. One plausible mechanism is by increasing testosterone concentration, which is established as an important factor for athletic performance. Therefore the aim of the study was to examine the relationship between plasma concentration of 25(OH)D and testosterone in Polish elite track and field athletes depending on vitamin D status, season, training period, body composition, sex, type of training, sun exposure and vitamin D supplementation. Plasma concentrations of 25(OH)D and testosterone were measured in all seasons within two years in athletes (70 females, 79 males) who represent strength (n = 103) and endurance (n = 46) kinds of sports, in the preparatorycompetitive season and transition period. There were no differences in 25(OH)D concentration between male and female athletes, insufficiency [25(OH)D < 30 ng/ml] was observed in 32.9%, whereas deficiency [25(OH)D < 20 ng/ ml] in 3.2%. Circannual rhythm was noted for vitamin D but not for testosterone concentration; no correlations between them were found either in strength or endurance athletes or between 25(OH)D and body composition. Testosterone concentration was higher in the transition period than in the preparatory-competition period only in male athletes. Higher 25(OH)D was observed in athletes who trained during winter in Africa (higher sun exposure) or used oral supplementation, whereas the respective testosterone levels were unchanged. In athletes, testosterone concentration did not reflect vitamin D status. The widespread of inadequate vitamin D status among athletes, makes it vital to recommend them the regular monitoring of 25(OH)D concentration and use of reasonable supplementation.
Keywords: Athletes; Exercise; Seasonal rhythm; Testosterone; Vitamin D status.
Copyright © Biology of Sport 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Seasonal Vitamin D Status in Polish Elite Athletes in Relation to Sun Exposure and Oral Supplementation.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 12;11(10):e0164395. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164395. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27732653 Free PMC article.
-
Circannual rhythm of plasmatic vitamin D levels and the association with markers of psychophysical stress in a cohort of Italian professional soccer players.Chronobiol Int. 2017;34(4):471-479. doi: 10.1080/07420528.2017.1297820. Epub 2017 Mar 17. Chronobiol Int. 2017. PMID: 28306393
-
Influence of Sunlight and Oral D3 Supplementation on Serum 25(OH)D Concentration and Exercise Performance in Elite Soccer Players.Nutrients. 2020 May 4;12(5):1311. doi: 10.3390/nu12051311. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32375348 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of vitamin D3 supplementation on serum 25(OH)D concentration and strength in athletes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2019 Nov 26;16(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s12970-019-0323-6. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2019. PMID: 31771586 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D and skeletal muscle function in athletes.Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2014 Nov;17(6):539-45. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000000105. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2014. PMID: 25137505 Review.
Cited by
-
Association Between Vitamin D Deficiency and Testosterone Levels in Adult Males: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2023 Sep 24;15(9):e45856. doi: 10.7759/cureus.45856. eCollection 2023 Sep. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37750061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypovitaminosis D in Young Basketball Players: Association with Jumping and Hopping Performance Considering Gender.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 May 19;18(10):5446. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18105446. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34069673 Free PMC article.
-
Seasonal changes in free 25-(OH)D and vitamin D metabolite ratios and their relationship with psychophysical stress markers in male professional football players.Front Physiol. 2023 Oct 16;14:1258678. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1258678. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37908338 Free PMC article.
-
Does vitamin D affect strength and speed characteristics and testosterone concentration in elite young track and field athletes in the North European summer?Nutr J. 2023 Mar 8;22(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12937-023-00848-7. Nutr J. 2023. PMID: 36882800 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and novel risk factors for vitamin D insufficiency in elite athletes: systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Nutr. 2022 Dec;61(8):3857-3871. doi: 10.1007/s00394-022-02967-z. Epub 2022 Jul 26. Eur J Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35882673 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pludowski P, Holick MF, Pilz S, Wagner CL, Hollis BW, Grant WB, Shoenfeld Y, Lerchbaum E, Llewellyn DJ, Kienreich K, Soni M. Vitamin D effects on musculoskeletal health, immunity, autoimmunity, cardiovascular disease, cancer, fertility, pregnancy, dementia and mortality – a review of recent evidence. Autoimmun Rev. 2013;12(10):976–89. - PubMed
-
- Blomberg Jensen M, Nielsen JE, Jorgensen A, Rajpert-De Meyts E, Kristensen DM, Jorgensen N, Skakkebaek NE, Juul A, Leffers H. Vitamin D receptor and vitamin D metabolizing enzymes are expressed in the human male reproductive tract. Hum Reprod. 2010;25(5):1303–11. - PubMed
-
- Anagnostis P, Karras S, Goulis DG. Vitamin D in human reproduction: A narrative review. Int J Clin Pract. 2013;67:225–235. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
