The Potential Diagnostic Value of Exosomal Long Noncoding RNAs in Solid Tumors: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review
- PMID: 32879887
- PMCID: PMC7448226
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/6786875
The Potential Diagnostic Value of Exosomal Long Noncoding RNAs in Solid Tumors: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: Exosomes are defined as small membranous vesicles. After RNA content was discovered in exosomes, they emerged as a novel approach for the treatment and diagnosis of cancer. Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNA), a kind of specific RNA transcript, have been reported to function as tumor growth, metastasis, invasion, and prognosis by regulating the tumor microenvironment in exosomes. This study aims at exploring the potential diagnostic of exosomal lncRNA in solid tumors.
Methods: A meta-analysis conducted from January 2000 to October 2019 identified publications in the English language. We searched all relevant English literature from the Web of Science, EMBASE, and PubMed databases through October 1, 2019. The articles were strictly screened by our criteria and critiqued using the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines.
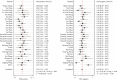
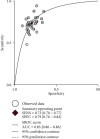
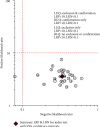
Results: There were 28 studies with 19 articles (4017 patients) identified, including studies on gastric cancer, laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma, colorectal cancer, cholangiocarcinoma, breast cancer, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, nonsmall cell lung cancer, and prostate cancer. A meta-analysis showed that the combined value of sensitivity in 29 studies was 0.74 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.7-0.78), and the combined value of specificity in the studies was 0.81 (95% CI, 0.78-0.83). This suggests the high diagnostic efficacy of liquid exosomes in cancer patients. It is statistically insignificant in terms of sex, ethnicity, and year. The diagnostic power of urinary system tumors was found to be higher than that of digestive system tumors by several subgroup analyses.
Conclusions: We performed a meta-analysis and literature review of 28 studies that included 4017 patients with 10 malignant cancer types. Mechanistically, our study demonstrated that lncRNAs in exosomes could be a promising bioindicator for the diagnosis and prognosis of solid tumors. INPLASY Registration Number: INPLASY202060083.
Copyright © 2020 Zilong Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Exosomal noncoding RNAs as noninvasive biomarkers in bladder cancer: a diagnostic meta-analysis.Clin Transl Oncol. 2024 Jun;26(6):1497-1507. doi: 10.1007/s12094-023-03374-4. Epub 2024 Jan 16. Clin Transl Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38227115 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-Derived Exosomal Long Noncoding RNAs as Promising Diagnostic Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;46(2):532-545. doi: 10.1159/000488620. Epub 2018 Mar 26. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29614511
-
Exosomal long noncoding RNA lnc-GNAQ-6:1 may serve as a diagnostic marker for gastric cancer.Clin Chim Acta. 2020 Feb;501:252-257. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.10.047. Epub 2019 Nov 12. Clin Chim Acta. 2020. PMID: 31730812
-
The diagnostic and prognostic value of exosome-derived long non-coding RNAs in cancer patients: a meta-analysis.Clin Exp Med. 2020 Aug;20(3):339-348. doi: 10.1007/s10238-020-00638-z. Epub 2020 Jun 5. Clin Exp Med. 2020. PMID: 32504320 Review.
-
Circulating long noncoding RNAs as potential biomarkers for stomach cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.World J Surg Oncol. 2021 Mar 26;19(1):89. doi: 10.1186/s12957-021-02194-6. World J Surg Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33771184 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Long non-coding RNA as a potential diagnostic biomarker in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2023 Sep 21;18(9):e0291921. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0291921. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37733767 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Breast Cancer: From Biology and Function to Clinical Diagnosis and Therapeutic Management.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 13;24(8):7208. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087208. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The diagnostic value of exosomal circular RNAs in cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Med. 2023 Jan;12(2):1709-1720. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5012. Epub 2022 Jul 25. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 35879835 Free PMC article.
-
Evolving Role of Exosomes in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery and Dermatology.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2024 Aug 16;12(8):e6061. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000006061. eCollection 2024 Aug. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2024. PMID: 39157711 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes in Lung Cancer: Actors and Heralds of Tumor Development.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Aug 27;13(17):4330. doi: 10.3390/cancers13174330. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34503141 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

