Chemical and Sensory Characteristics of Soy Sauce: A Review
- PMID: 32880168
- PMCID: PMC7581291
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c04274
Chemical and Sensory Characteristics of Soy Sauce: A Review
Abstract
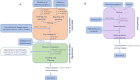
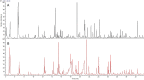
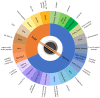
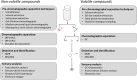
Soy sauce is a fermented product, and its flavor is a complex mixture of individual senses which, in combination, create a strong palatable condiment for many Eastern and Western dishes. This Review focuses on our existing knowledge of the chemical compounds present in soy sauce and their potential relevance to the flavor profile. Taste is dominated by umami and salty sensations. Free amino acids, nucleotides, and small peptides are among the most important taste-active compounds. Aroma is characterized by caramel-like, floral, smoky, malty, and cooked potato-like odors. Aroma-active volatiles are chemically diverse including acids, alcohols, aldehydes, esters, furanones, pyrazines, and S-compounds. The origin of all compounds relates to both the raw ingredients and starter cultures used as well as the parameters applied during production. We are only just starting to help develop innovative studies where we can combine different analytical platforms and chemometric analysis to link flavor attributes to chemical composition.
Keywords: Maillard reactions; aroma; fermented; gas chromatography−mass spectrometry (GC-MS); liquid chromatography−mass spectrometry (LC-MS); soy sauce; taste.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Greenberg P. Soy Sauce, China’s Liquid Spice. Sauces, Seas. Spices 2000, 7 (2), 21–22.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

