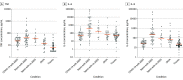
Cytokine Levels in Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19 and Other Conditions
- PMID: 32880615
- PMCID: PMC7489366
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2020.17052
Cytokine Levels in Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19 and Other Conditions
Abstract
This study compares levels of tumor necrosis factor α, IL-6, and IL-8 in critically ill patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vs those with other critical illness to better characterize the contribution of cytokine storm to COVID-19 pathophysiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures