Synthetic biology, combinatorial biosynthesis, and chemo‑enzymatic synthesis of isoprenoids
- PMID: 32880770
- PMCID: PMC7666032
- DOI: 10.1007/s10295-020-02306-3
Synthetic biology, combinatorial biosynthesis, and chemo‑enzymatic synthesis of isoprenoids
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Synthetic biology, combinatorial biosynthesis, and chemo-enzymatic synthesis of isoprenoids.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Dec;47(12):1181. doi: 10.1007/s10295-020-02327-y. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 33180238 No abstract available.
Abstract
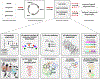
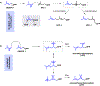
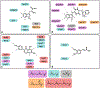
Isoprenoids are a large class of natural products with myriad applications as bioactive and commercial compounds. Their diverse structures are derived from the biosynthetic assembly and tailoring of their scaffolds, ultimately constructed from two C5 hemiterpene building blocks. The modular logic of these platforms can be harnessed to improve titers of valuable isoprenoids in diverse hosts and to produce new-to-nature compounds. Often, this process is facilitated by the substrate or product promiscuity of the component enzymes, which can be leveraged to produce novel isoprenoids. To complement rational enhancements and even re-programming of isoprenoid biosynthesis, high-throughput approaches that rely on searching through large enzymatic libraries are being developed. This review summarizes recent advances and strategies related to isoprenoid synthetic biology, combinatorial biosynthesis, and chemo-enzymatic synthesis, focusing on the past 5 years. Emerging applications of cell-free biosynthesis and high-throughput tools are included that culminate in a discussion of the future outlook and perspective of isoprenoid biosynthetic engineering.
Keywords: Combinatorial biosynthesis; Hemiterpenes; Isoprenoids; Synthetic biology; Terpenes.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Protein engineering for natural product biosynthesis and synthetic biology applications.Protein Eng Des Sel. 2021 Feb 15;34:gzab015. doi: 10.1093/protein/gzab015. Protein Eng Des Sel. 2021. PMID: 34137436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Artificial Pathway for Isoprenoid Biosynthesis Decoupled from Native Hemiterpene Metabolism.ACS Synth Biol. 2019 Feb 15;8(2):232-238. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.8b00383. Epub 2019 Jan 16. ACS Synth Biol. 2019. PMID: 30648856 Free PMC article.
-
Probing the Substrate Promiscuity of Isopentenyl Phosphate Kinase as a Platform for Hemiterpene Analogue Production.Chembiochem. 2019 Sep 2;20(17):2217-2221. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201900135. Epub 2019 Jul 22. Chembiochem. 2019. PMID: 30998839 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic engineering and synthetic biology approaches driving isoprenoid production in Escherichia coli.Bioresour Technol. 2017 Oct;241:430-438. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.05.168. Epub 2017 May 29. Bioresour Technol. 2017. PMID: 28599221 Review.
-
Metabolic engineering and synthetic biology for isoprenoid production in Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Jan;105(2):457-475. doi: 10.1007/s00253-020-11040-w. Epub 2021 Jan 4. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33394155 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances, opportunities, and challenges in methods for interrogating the structure activity relationships of natural products.Nat Prod Rep. 2024 Oct 17;41(10):1543-1578. doi: 10.1039/d4np00009a. Nat Prod Rep. 2024. PMID: 38912779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Engineering of the Isopentenol Utilization Pathway Enhanced the Production of Terpenoids in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.Mar Drugs. 2022 Sep 15;20(9):577. doi: 10.3390/md20090577. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 36135766 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Basis for the Substrate Promiscuity of Isopentenyl Phosphate Kinase from Candidatus methanomethylophilus alvus.ACS Chem Biol. 2022 Jan 21;17(1):85-102. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.1c00655. Epub 2021 Dec 14. ACS Chem Biol. 2022. PMID: 34905349 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Biosynthesis of Natural Products from Marine Microorganisms.Microorganisms. 2021 Dec 10;9(12):2551. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9122551. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34946152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein engineering for natural product biosynthesis and synthetic biology applications.Protein Eng Des Sel. 2021 Feb 15;34:gzab015. doi: 10.1093/protein/gzab015. Protein Eng Des Sel. 2021. PMID: 34137436 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cox-Georgian D, Ramadoss N, Dona C, Basu C (2019) Therapeutic and medicinal uses of terpenes In: Medicinal Plants: From Farm to Pharmacy. Springer International Publishing, pp 333–359
-
- Tetali SD (2019) Terpenes and isoprenoids: a wealth of compounds for global use. Planta 249:1–8 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

