Molecular dynamics study with mutation shows that N-terminal domain structural re-orientation in Niemann-Pick type C1 is required for proper alignment of cholesterol transport
- PMID: 32880929
- PMCID: PMC7461377
- DOI: 10.1111/jnc.15150
Molecular dynamics study with mutation shows that N-terminal domain structural re-orientation in Niemann-Pick type C1 is required for proper alignment of cholesterol transport
Abstract
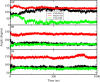
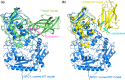
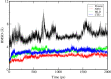
The lysosomal membrane protein Niemann-Pick type C1 (NPC1) and Niemann-Pick type C2 (NPC2) are main players of cholesterol control in the lysosome and it is known that the mutation on these proteins leads to the cholesterol trafficking-related neurodegenerative disease, which is called the NPC disease. The mutation R518W or R518Q on the NPC1 is one of the type of disease-related mutation that causes cholesterol transports to be cut in half, which results in the accumulation of cholesterol and lipids in the late endosomal/lysosomal compartment of the cell. Even though there has been significant progress with understanding the cholesterol transport by NPC1 in combination with NPC2, especially after the structural determination of the full-length NPC1 in 2016, many details such as the interaction of the full-length NPC1 with the NPC2, the molecular motions responsible for the cholesterol transport during and after this interaction, and the structure and the function relations of many mutations are still not well understood. In this study, we report the extensive molecular dynamics simulations in order to gain insight into the structure and the dynamics of NPC1 lumenal domain for the cholesterol transport and the disease behind the mutation (R518W). It was found that the mutation induces a structural shift of the N-terminal domain, toward the loop region in the middle lumenal domain, which is believed to play a central role in the interaction with NPC2 protein, so the interaction with the NPC2 protein might be less favorable compared to the wild NPC1. Also, the simulation indicates the possible re-orientation of the N-terminal domain with both the wild and the R518W-mutated NPC1 after receiving the cholesterol from the NPC2 that align to form an internal tunnel, which is a possible pose for further action in cholesterol trafficking. We believe the current study can provide a better understanding of the cholesterol transport by NPC1 especially the role of NTD of NPC1 in combination with NPC2 interactions.
Keywords: COVID-19; NPC1; NPC2; R518W mutant; cholesterol trafficking; molecular dynamics simulation; neurodegenerative Niemann-Pick C disease.
© 2020 International Society for Neurochemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
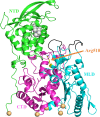





Similar articles
-
The point mutation of the cholesterol trafficking membrane protein NPC1 may affect its proper function in more than a single step: Molecular dynamics simulation study.Comput Biol Chem. 2022 Aug;99:107725. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2022.107725. Epub 2022 Jul 9. Comput Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35850050
-
Niemann-Pick C1 functions independently of Niemann-Pick C2 in the initial stage of retrograde transport of membrane-impermeable lysosomal cargo.J Biol Chem. 2010 Feb 12;285(7):4983-94. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.037622. Epub 2009 Dec 10. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20007703 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary abnormalities in animal models due to Niemann-Pick type C1 (NPC1) or C2 (NPC2) disease.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 2;8(7):e67084. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067084. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23843985 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and Molecular Features of Early Infantile Niemann Pick Type C Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 17;21(14):5059. doi: 10.3390/ijms21145059. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32709131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Finding pathogenic commonalities between Niemann-Pick type C and other lysosomal storage disorders: Opportunities for shared therapeutic interventions.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020 Oct 1;1866(10):165875. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165875. Epub 2020 Jun 6. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020. PMID: 32522631 Review.
Cited by
-
The Antifungal Antibiotic Filipin as a Diagnostic Tool of Cholesterol Alterations in Lysosomal Storage Diseases and Neurodegenerative Disorders.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Jan 9;12(1):122. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12010122. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36671323 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

