Activity-Based Protein Profiling (ABPP) of Oxidoreductases
- PMID: 32881211
- PMCID: PMC7894341
- DOI: 10.1002/cbic.202000542
Activity-Based Protein Profiling (ABPP) of Oxidoreductases
Abstract
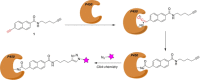
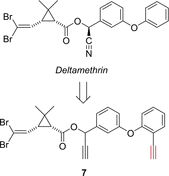
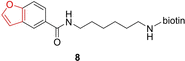
Over the last two decades, activity-based protein profiling (ABPP) has been established as a tremendously useful proteomic tool for measuring the activity of proteins in their cellular context, annotating the function of uncharacterized proteins, and investigating the target profile of small-molecule inhibitors. Unlike hydrolases and other enzyme classes, which exhibit a characteristic nucleophilic residue, oxidoreductases have received much less attention in ABPP. In this minireview, the state of the art of ABPP of oxidoreductases is described and the scope and limitations of the existing approaches are discussed. It is noted that several ABPP probes have been described for various oxidases, but none so far for a reductase, which gives rise to opportunities for future research.
Keywords: chemical proteomics; covalent inhibitors; drug discovery; oxidoreductases; proteomics.
© 2020 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
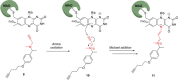
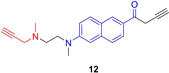
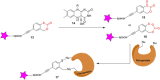

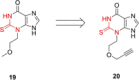
Similar articles
-
[Advances in applications of activity-based chemical probes in the characterization of amino acid reactivities].Se Pu. 2023 Jan;41(1):14-23. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2022.05013. Se Pu. 2023. PMID: 36633073 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
ABPP-CoDEL: Activity-Based Proteome Profiling-Guided Discovery of Tyrosine-Targeting Covalent Inhibitors from DNA-Encoded Libraries.J Am Chem Soc. 2023 Nov 22;145(46):25283-25292. doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c08852. Epub 2023 Oct 19. J Am Chem Soc. 2023. PMID: 37857329
-
A general approach for activity-based protein profiling of oxidoreductases with redox-differentiated diarylhalonium warheads.Chem Sci. 2025 Mar 11;16(15):6240-6256. doi: 10.1039/d4sc08454c. eCollection 2025 Apr 9. Chem Sci. 2025. PMID: 40103729 Free PMC article.
-
Proteome-Wide Data Guides the Discovery of Lysine-Targeting Covalent Inhibitors Using DNA-Encoded Chemical Libraries.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025 Jun 17;64(25):e202505581. doi: 10.1002/anie.202505581. Epub 2025 Apr 24. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025. PMID: 40223230
-
Activity- and reactivity-based proteomics: Recent technological advances and applications in drug discovery.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2021 Feb;60:20-29. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2020.06.011. Epub 2020 Aug 5. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2021. PMID: 32768892 Review.
Cited by
-
Activity-Based Protein Profiling of Serine Hydrolases in Bacteria: Methods and Protocols.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2921:57-72. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4502-4_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40515984
-
Probing Monotopic Phosphoglycosyl Transferases from Complex Cellular Milieu.ACS Chem Biol. 2022 Nov 18;17(11):3191-3197. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.2c00648. Epub 2022 Nov 8. ACS Chem Biol. 2022. PMID: 36346917 Free PMC article.
-
Photoaffinity probe-enabled discovery of sennoside A reductase in Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum.J Pharm Anal. 2025 Jan;15(1):101108. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2024.101108. Epub 2024 Sep 21. J Pharm Anal. 2025. PMID: 39902460 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Approaches to Study SARS-CoV-2 Biology and COVID-19 Pathology.J Proteome Res. 2021 Feb 5;20(2):1133-1152. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.0c00764. Epub 2021 Jan 19. J Proteome Res. 2021. PMID: 33464917 Free PMC article.
-
Activity-Based Protein Profiling of Bacterial Monooxygenases.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2921:293-317. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4502-4_16. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40515997
References
-
- November J., J. History Biol. 2018, 51, 807–840. - PubMed
-
- Müller J. B., Geyer P. E., Colaço A. R., Treit P. V., Strauss M. T., Oroshi M., Doll S., Virreira Winter S., Bader J. M., Köhler N., Theis F., Santos A., Mann M., Nature 2020, 582, 592–596. - PubMed
-
- Greenbaum D., Medzihradszky K. F., Burlingame A., Bogyo M., Chem. Biol. 2000, 7, 569–581. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

