Estimated Radiation Doses Received by New Mexico Residents from the 1945 Trinity Nuclear Test
- PMID: 32881738
- PMCID: PMC7497485
- DOI: 10.1097/HP.0000000000001328
Estimated Radiation Doses Received by New Mexico Residents from the 1945 Trinity Nuclear Test
Abstract
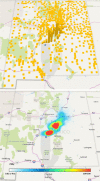
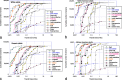
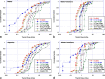
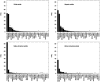
The National Cancer Institute study of projected health risks to New Mexico residents from the 1945 Trinity nuclear test provides best estimates of organ radiation absorbed doses received by representative persons according to ethnicity, age, and county. Doses to five organs/tissues at significant risk from exposure to radioactive fallout (i.e., active bone marrow, thyroid gland, lungs, stomach, and colon) from the 63 most important radionuclides in fresh fallout from external and internal irradiation were estimated. The organ doses were estimated for four resident ethnic groups in New Mexico (Whites, Hispanics, Native Americans, and African Americans) in seven age groups using: (1) assessment models described in a companion paper, (2) data on the spatial distribution and magnitude of radioactive fallout derived from historical documents, and (3) data collected on diets and lifestyles in 1945 from interviews and focus groups conducted in 2015-2017 (described in a companion paper). The organ doses were found to vary widely across the state with the highest doses directly to the northeast of the detonation site and at locations close to the center of the Trinity fallout plume. Spatial heterogeneity of fallout deposition was the largest cause of variation of doses across the state with lesser differences due to age and ethnicity, the latter because of differences in diets and lifestyles. The exposure pathways considered included both external irradiation from deposited fallout and internal irradiation via inhalation of airborne radionuclides in the debris cloud as well as resuspended ground activity and ingestion of contaminated drinking water (derived both from rivers and rainwater cisterns) and foodstuffs including milk products, beef, mutton, and pork, human-consumed plant products including leafy vegetables, fruit vegetables, fruits, and berries. Tables of best estimates of county population-weighted average organ doses by ethnicity and age are presented. A discussion of our estimates of uncertainty is also provided to illustrate a lower and upper credible range on our best estimates of doses. Our findings indicate that only small geographic areas immediately downwind to the northeast received exposures of any significance as judged by their magnitude relative to natural radiation. The findings presented are the most comprehensive and well-described estimates of doses received by populations of New Mexico from the Trinity nuclear test.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The Likelihood of Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes and Genetic Disease (Transgenerational Effects) from Exposure to Radioactive Fallout from the 1945 Trinity Atomic Bomb Test.Health Phys. 2020 Oct;119(4):494-503. doi: 10.1097/HP.0000000000001170. Health Phys. 2020. PMID: 32881736 Free PMC article.
-
The Methodology Used to Assess Doses from the First Nuclear Weapons Test (Trinity) to the Populations of New Mexico.Health Phys. 2020 Oct;119(4):400-427. doi: 10.1097/HP.0000000000001331. Health Phys. 2020. PMID: 32881739 Free PMC article.
-
Projected Cancer Risks to Residents of New Mexico from Exposure to Trinity Radioactive Fallout.Health Phys. 2020 Oct;119(4):478-493. doi: 10.1097/HP.0000000000001333. Health Phys. 2020. PMID: 32881740 Free PMC article.
-
Review of methods of dose estimation for epidemiological studies of the radiological impact of nevada test site and global fallout.Radiat Res. 2006 Jul;166(1 Pt 2):209-18. doi: 10.1667/RR3172.1. Radiat Res. 2006. PMID: 16808609 Review.
-
Historical overview of atmospheric nuclear weapons testing and estimates of fallout in the continental United States.Health Phys. 2002 May;82(5):591-608. doi: 10.1097/00004032-200205000-00007. Health Phys. 2002. PMID: 12003011 Review.
Cited by
-
The Likelihood of Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes and Genetic Disease (Transgenerational Effects) from Exposure to Radioactive Fallout from the 1945 Trinity Atomic Bomb Test.Health Phys. 2020 Oct;119(4):494-503. doi: 10.1097/HP.0000000000001170. Health Phys. 2020. PMID: 32881736 Free PMC article.
-
Dose Coefficients for Internal Dose Assessments for Exposure to Radioactive Fallout.Health Phys. 2022 Jan 1;122(1):125-235. doi: 10.1097/HP.0000000000001500. Health Phys. 2022. PMID: 34898518 Free PMC article.
-
Parameter Values for Estimation of Internal Doses from Ingestion of Radioactive Fallout from Nuclear Detonations.Health Phys. 2022 Jan 1;122(1):236-268. doi: 10.1097/HP.0000000000001493. Health Phys. 2022. PMID: 34898519 Free PMC article.
-
Accounting for Unfissioned Plutonium from the Trinity Atomic Bomb Test.Health Phys. 2020 Oct;119(4):504-516. doi: 10.1097/HP.0000000000001146. Health Phys. 2020. PMID: 32881735 Free PMC article.
-
The Methodology Used to Assess Doses from the First Nuclear Weapons Test (Trinity) to the Populations of New Mexico.Health Phys. 2020 Oct;119(4):400-427. doi: 10.1097/HP.0000000000001331. Health Phys. 2020. PMID: 32881739 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anspaugh L, Church B. Historical estimates of external gamma exposure and collective external gamma exposure from testing at the Nevada Test Site. I. Test Series through Hardtack II, 1958. Health Phys 51:35–51; 1986. - PubMed
-
- Beck HL, Anspaugh LR, Bouville A, Simon SL. Review of methods of dose estimation for epidemiological studies of the radiological impact of NTS and Global Fallout. Radiat Res 166:209–218; 2006. - PubMed
-
- Bouville A, Beck HL. The HASL gummed-film network and its use in the reconstruction of doses resulting from nuclear weapons tests. Technol 7:355–362; 2000.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

