Quercetin enhances motility in aged and heat-stressed Caenorhabditis elegans nematodes by modulating both HSF-1 activity, and insulin-like and p38-MAPK signalling
- PMID: 32881908
- PMCID: PMC7470330
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0238528
Quercetin enhances motility in aged and heat-stressed Caenorhabditis elegans nematodes by modulating both HSF-1 activity, and insulin-like and p38-MAPK signalling
Abstract
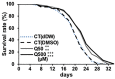
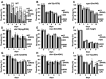
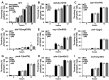
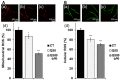
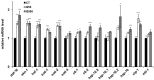
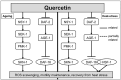
Quercetin is a yellow pigment that is found in many common dietary plants, and that protects against oxidative stress, inflammation, and arteriosclerosis. It has also been suggested to prolong the lifespan of, and enhance heat-stress tolerance in nematodes; thus, the present study investigated its effects on both the nematode life- and health span by assessing its capacity to promote nematode motility after aging and/or heat stress, as well as the mechanisms underlying these effects. The results of the conducted analyses showed that quercetin feeding prolonged lifespan, suppressed age-related motility retardation, improved motility recovery after heat stress, and decreased the production of both intercellular and mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in the analysed Caenorhabditis elegans strains, likely by modulating the insulin-like signalling (ILS) pathway and p38-mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. In particular, the transcription factors DAF-16 and SKN-1 were found to mediate the observed quercetin-induced effects, consistent with their previously demonstrated roles as regulators of aging. Furthermore, we demonstrated, for the first time, that quercetin induced heat-stress tolerance in C. elegans by modulating HSF-1 expression and/or activity. Thus, the present study provides valuable insights into the mechanisms by which quercetin inhibit aging and enhance heat-stress tolerance via ILS and MAPK pathway in C. elegans.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

