A Membrane-Bound Diacylglycerol Species Induces PKCϵ-Mediated Hepatic Insulin Resistance
- PMID: 32882164
- PMCID: PMC7544641
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.08.001
A Membrane-Bound Diacylglycerol Species Induces PKCϵ-Mediated Hepatic Insulin Resistance
Abstract
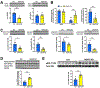
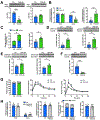
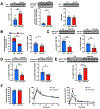
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is strongly associated with hepatic insulin resistance (HIR); however, the key lipid species and molecular mechanisms linking these conditions are widely debated. We developed a subcellular fractionation method to quantify diacylglycerol (DAG) stereoisomers and ceramides in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), mitochondria, plasma membrane (PM), lipid droplets, and cytosol. Acute knockdown (KD) of diacylglycerol acyltransferase-2 in liver induced HIR in rats. This was due to PM sn-1,2-DAG accumulation, which promoted PKCϵ activation and insulin receptor kinase (IRK)-T1160 phosphorylation, resulting in decreased IRK-Y1162 phosphorylation. Liver PM sn-1,2-DAG content and IRK-T1160 phosphorylation were also higher in humans with HIR. In rats, liver-specific PKCϵ KD ameliorated high-fat diet-induced HIR by lowering IRK-T1160 phosphorylation, while liver-specific overexpression of constitutively active PKCϵ-induced HIR by promoting IRK-T1160 phosphorylation. These data identify PM sn-1,2-DAGs as the key pool of lipids that activate PKCϵ and that hepatic PKCϵ is both necessary and sufficient in mediating HIR.
Keywords: ceramides; dicylglycerols; hepatic glucose production; hepatic glycogen synthesis; hepatic insulin resistance; insulin receptor phosphorylation; liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry; nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; protein kinase C-epsilon; type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Boni LT, and Rando RR (1985). The nature of protein kinase C activation by physically defined phospholipid vesicles and diacylglycerols. J Biol Chem 260, 10819–10825. - PubMed
-
- Brandon AE, Liao BM, Diakanastasis B, Parker BL, Raddatz K, McManus SA, O’Reilly L, Kimber E, van der Kraan AG, Hancock D, et al. (2019). Protein Kinase C Epsilon Deletion in Adipose Tissue, but Not in Liver, Improves Glucose Tolerance. Cell Metab 29, 183–191 e187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

