Oral manifestations in a patient with a history of asymptomatic COVID-19: Case report
- PMID: 32882435
- PMCID: PMC7462545
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.08.071
Oral manifestations in a patient with a history of asymptomatic COVID-19: Case report
Abstract
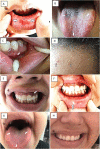
The pandemic situation has led to public health measures that have forced patients with and without the SARS-CoV-2 virus to remain isolated and take steps to prevent the spread. Many of these patients have been unable to attend the control of medical-dental services, which in many cases complicates their situation. This study reports on the oral manifestations of an asymptomatic COVID-19 patient treated interdisciplinary by teleconsultation due to the sudden appearance of lesions in the oral mucosa. Lesions are diagnosed, therapeutic measures are taken, and improvement is shown. This case shows that the problems that arise in the oral mucosa in patients with suspected or confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection can be monitored through interdisciplinary teleconsultation during the pandemic with the support of information technology currently available worldwide. It also decreases the risk of transmission of SARS-Cov-2 between patients and health professionals.
Keywords: COVID-19; Candidiasis; Case report; Hyperpigmentation; Melanin; Oral mucosa; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Association CPM An update on the epidemiological characteristics of novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19) Chin J Epidemiol. 2020;41(2):139–144. - PubMed
-
- Carreras-Presas C.M., Sánchez J.A., López-Sánchez A.F., Jané-Salas E., Pérez M.L.S. Oral vesiculobullous lesions associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Oral Dis. 2020 doi: 10.1111/odi.13382. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/odi.13382 [Cited 15 July 2020]. Available from: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

