Circulating Plasminogen Concentration at Admission in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)
- PMID: 32882718
- PMCID: PMC7645831
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0040-1715454
Circulating Plasminogen Concentration at Admission in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)
Conflict of interest statement
None.
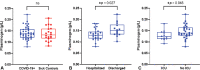
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hemostasis profile in COVID-19 infection.Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2020 May;66(5):571-572. doi: 10.1590/1806-9282.66.5.571. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2020. PMID: 32638971 No abstract available.
-
COVID-19 coagulopathy vs disseminated intravascular coagulation.Blood Adv. 2020 Jun 23;4(12):2850. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020002197. Blood Adv. 2020. PMID: 32574369 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Coronavirus Disease 2019 Coagulopathy: Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation and Thrombotic Microangiopathy-Either, Neither, or Both.Semin Thromb Hemost. 2020 Oct;46(7):781-784. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1712156. Epub 2020 Jun 8. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2020. PMID: 32512589 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Coronavirus Disease 2019: The Role of the Fibrinolytic System from Transmission to Organ Injury and Sequelae.Semin Thromb Hemost. 2020 Oct;46(7):841-844. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1709996. Epub 2020 May 9. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2020. PMID: 32386428 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Correlation of indirect markers of hypercoagulability with thromboelastography in severe coronavirus 2019.Thromb Res. 2020 Nov;195:69-71. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2020.07.013. Epub 2020 Jul 9. Thromb Res. 2020. PMID: 32659463 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Endothelial, Immunothrombotic, and Inflammatory Biomarkers in the Risk of Mortality in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: The Role of Dexamethasone.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Jul 13;11(7):1249. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11071249. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34359331 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacotherapy consideration of thrombolytic medications in COVID-19-associated ARDS.J Intensive Care. 2022 Jul 30;10(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s40560-022-00625-4. J Intensive Care. 2022. PMID: 35908022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low level of plasminogen increases risk for mortality in COVID-19 patients.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Aug 5;12(8):773. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04070-3. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34354045 Free PMC article.
-
Plasminogen missense variants and their involvement in cardiovascular and inflammatory disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Jun 25;11:1406953. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1406953. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38984351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Prothrombotic State Associated with SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Pathophysiological Aspects.Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2021 Jul 1;13(1):e2021045. doi: 10.4084/MJHID.2021.045. eCollection 2021. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34276914 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Henry B M, de Oliveira M HS, Benoit S, Plebani M, Lippi G. Hematologic, biochemical and immune biomarker abnormalities associated with severe illness and mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a meta-analysis. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2020;58(07):1021–1028. - PubMed
-
- Wright F L, Vogler T O, Moore E E.Fibrinolysis shutdown correlation with thromboembolic events in severe COVID-19 infectionJ Am Coll Surg2020; Doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2020.05.007 (epub ahead of print)

