Natural Flavonoids as Potential Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Inhibitors for Anti-SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 32882868
- PMCID: PMC7504743
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25173980
Natural Flavonoids as Potential Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Inhibitors for Anti-SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
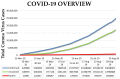
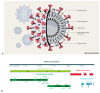
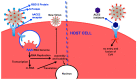
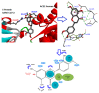
Over the years, coronaviruses (CoV) have posed a severe public health threat, causing an increase in mortality and morbidity rates throughout the world. The recent outbreak of a novel coronavirus, named severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) caused the current Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic that affected more than 215 countries with over 23 million cases and 800,000 deaths as of today. The situation is critical, especially with the absence of specific medicines or vaccines; hence, efforts toward the development of anti-COVID-19 medicines are being intensively undertaken. One of the potential therapeutic targets of anti-COVID-19 drugs is the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). ACE2 was identified as a key functional receptor for CoV associated with COVID-19. ACE2, which is located on the surface of the host cells, binds effectively to the spike protein of CoV, thus enabling the virus to infect the epithelial cells of the host. Previous studies showed that certain flavonoids exhibit angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition activity, which plays a crucial role in the regulation of arterial blood pressure. Thus, it is being postulated that these flavonoids might also interact with ACE2. This postulation might be of interest because these compounds also show antiviral activity in vitro. This article summarizes the natural flavonoids with potential efficacy against COVID-19 through ACE2 receptor inhibition.
Keywords: ACE2; COVID-19; coronavirus; flavonoid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), SARS-CoV-2 and the pathophysiology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).J Pathol. 2020 Jul;251(3):228-248. doi: 10.1002/path.5471. Epub 2020 Jun 10. J Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32418199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 pandemic and research gaps: Understanding SARS-CoV-2 interaction with the ACE2 receptor and implications for therapy.Theranostics. 2020 Jun 12;10(16):7448-7464. doi: 10.7150/thno.48076. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32642005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Organ-protective effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and its effect on the prognosis of COVID-19.J Med Virol. 2020 Jul;92(7):726-730. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25785. Epub 2020 Apr 5. J Med Virol. 2020. PMID: 32221983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and the renin-angiotensin system: A closer look at angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2).Ann Clin Biochem. 2020 Sep;57(5):339-350. doi: 10.1177/0004563220928361. Epub 2020 Jun 2. Ann Clin Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32369402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design of Potent Membrane Fusion Inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2, an Emerging Coronavirus with High Fusogenic Activity.J Virol. 2020 Jul 1;94(14):e00635-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00635-20. Print 2020 Jul 1. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32376627 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Antiseptics: An expeditious third force in the prevention and management of coronavirus diseases.Curr Res Microb Sci. 2024 Oct 16;7:100293. doi: 10.1016/j.crmicr.2024.100293. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Microb Sci. 2024. PMID: 39497935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Neurological Manifestations of Coronaviruses by Candidate Phytochemicals: A Mechanistic Approach.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jan 20;11:621099. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.621099. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33708124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The direct and indirect effects of bioactive compounds against coronavirus.Food Front. 2022 Mar;3(1):96-123. doi: 10.1002/fft2.119. Epub 2021 Dec 8. Food Front. 2022. PMID: 35462942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Solanum nigrum L. in COVID-19 and post-COVID complications: a propitious candidate.Mol Cell Biochem. 2023 Oct;478(10):2221-2240. doi: 10.1007/s11010-022-04654-3. Epub 2023 Jan 23. Mol Cell Biochem. 2023. PMID: 36689040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic and prophylactic effect of flavonoids in post-COVID-19 therapy.Phytother Res. 2022 May;36(5):2042-2060. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7436. Epub 2022 Mar 18. Phytother Res. 2022. PMID: 35302260 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chhikara B.S., Rathi B., Singh J., Poonam F. Corona virus SARS-CoV-2 disease COVID-19: Infection, prevention and clinical advances of the prospective chemical drug therapeutics. Chem. Biol. Lett. 2020;7:63–72.
-
- World Health Organization Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report—70. [(accessed on 2 May 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio...
-
- World Health Organization WHO Director-General’s Opening Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19—11 March 2020. [(accessed on 23 April 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-re....
-
- Welt F.G., Shah P.B., Aronow H.D., Bortnick A.E., Henry T.D., Sherwood M.W., Young M.N., Davidson L.J., Kadavath S., Mahmud E. Catheterization laboratory considerations during the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic: From ACC’s Interventional Council and SCAI. J. Am. Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:2372–2375. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.03.021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

