Lenalidomide in Combination with Arsenic Trioxide: an Effective Therapy for Primary Effusion Lymphoma
- PMID: 32883022
- PMCID: PMC7563318
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12092483
Lenalidomide in Combination with Arsenic Trioxide: an Effective Therapy for Primary Effusion Lymphoma
Abstract
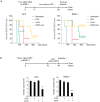
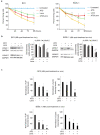
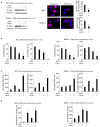
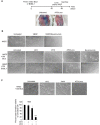
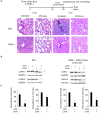
Primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) is a rare aggressive subset of non-Hodgkin B cell lymphoma. PEL is secondary to Kaposi sarcoma herpes virus (KSHV) and predominantly develops in serous cavities. Conventional chemotherapy remains the treatment of choice for PEL and yields high response rates with no significant comorbidities. Yet, chemotherapy often fails in achieving or maintaining long-term remission. Lenalidomide (Lena), an immunomodulatory drug, displayed some efficacy in the treatment of PEL. On the other hand, arsenic trioxide (ATO) in combination with other agents effectively treated a number of blood malignancies, including PEL. In this study, we present evidence that the combination of ATO/Lena significantly enhanced survival of PEL mice, decreased the volume of exacerbated ascites in the peritoneum, and reduced tumor infiltration in organs of treated animals. In ex vivo treated PEL cells, ATO/Lena decreased the proliferation and downregulated the expression of KSHV latent viral proteins. This was associated with decreased NF-κB activation, resulting in reactivation of viral replication, downregulation of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and IL-10, inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor, and apoptosis. Our results elucidate the mechanism of action of ATO/Lena and present it as a promising targeted therapeutic modality in PEL management, which warrants further clinical investigation.
Keywords: HHV-8; LANA; immunomodulatory drugs; latent cycle; lymphoma; lytic cycle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Katano H. Pathological Features of Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Infection. In: Kawaguchi Y., Mori Y., Kimura H., editors. Human Herpesviruses. Springer; Singapore: 2018. pp. 357–376. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

