A Highly Polymorphic Panel Consisting of Microhaplotypes and Compound Markers with the NGS and Its Forensic Efficiency Evaluations in Chinese Two Groups
- PMID: 32883034
- PMCID: PMC7565596
- DOI: 10.3390/genes11091027
A Highly Polymorphic Panel Consisting of Microhaplotypes and Compound Markers with the NGS and Its Forensic Efficiency Evaluations in Chinese Two Groups
Abstract
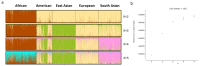
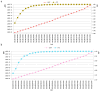
Novel genetic markers like microhaplotypes and compound markers show promising potential in forensic research. Based on previously reported single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and insertion/deletion (InDel) polymorphism loci, 29 genetic markers including 22 microhaplotypes and seven compound markers were identified. Genetic distributions of the 29 loci in five continental populations, Kazak and Mongolian groups in China were investigated. We found that the expected heterozygosity values of these 29 loci were >0.4 in these populations, indicating these loci were relatively high polymorphisms. Population genetic analyses of five continental populations showed that five loci displayed relatively high genetic variations among these continental populations and could be useful markers for ancestry analysis. In summary, the 29 loci displayed relatively high genetic diversities in continental populations and Chinese two groups and could be informative loci for forensic research.
Keywords: Kazak; Mongolian; compound marker; forensic research; microhaplotype.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors stated that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


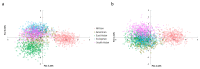

References
-
- Wang Z., Lu B., Jin X., Yan J., Meng H., Zhu B. Genetic and structural characterization of 20 autosomal short tandem repeats in the Chinese Qinghai Han population and its genetic relationships and interpopulation differentiations with other reference populations. Forensic Sci. Res. 2018;3:145–152. doi: 10.1080/20961790.2018.1485199. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Avent I., Kinnane A.G., Jones N., Petermann I., Daniel R., Gahan M.E., McNevin D. The QIAGEN 140-locus single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) panel for forensic identification using massively parallel sequencing (MPS): An evaluation and a direct-to-PCR trial. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2019;133:677–688. doi: 10.1007/s00414-018-1975-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

