Prognostic analysis of patients with non-small cell lung cancer harboring exon 19 or 21 mutation in the epidermal growth factor gene and brain metastases
- PMID: 32883221
- PMCID: PMC7469092
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-020-07249-7
Prognostic analysis of patients with non-small cell lung cancer harboring exon 19 or 21 mutation in the epidermal growth factor gene and brain metastases
Abstract
Background: In 1997, the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) put forward the recursive partitioning analysis classification for the prognosis of brain metastases (BMs), but this system does not take into account the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations. The aim of the study is to assess the prognosis of patients with EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and BMs in the era of tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) availability.
Methods: This was a retrospective study of consecutive patients with EGFR-mutated (exon 19 or 21) NSCLC diagnosed between 01/2011 and 12/2014 at the Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute & Hospital and who were ultimately diagnosed with BMs. The patients were stage I-III at initial presentation and developed BMs as the first progression. Overall survival (OS), OS after BM diagnosis (mOS), intracranial progression-free survival (iPFS), response to treatment, and adverse reactions were analyzed.
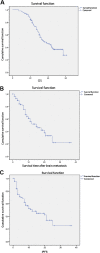
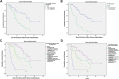
Results: Median survival was 35 months, and the 1- and 2- year survival rates were 95.6% (108/113) and 74.3% (84/113). The 3-month CR + PR rates of radiotherapy(R), chemotherapy(C), targeted treatment(T), and targeted treatment + radiotherapy(T+R) after BMs were 63.0% (17/27), 26.7% (4/15), 50.0% (7/14), and 89.7% (35/39), respectively. The median survival of the four treatments was 20, 9, 12, and 25 months after BMs, respectively (P = 0.001). Multivariable analysis showed that < 3 BMs (odds ratio (OR) = 3.34, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.89-5.91, P < 0.001) and treatment after BMs (OR = 0.68, 95%CI: 0.54-0.85, P = 0.001) were independently associated with better prognosis.
Conclusions: The prognosis of patients with NSCLC and EGFR mutation in exon 19 or 21 after BM is associated with the number of brain metastasis and the treatment method. Targeted treatment combined with radiotherapy may have some advantages over other treatments, but further study is warranted to validate the results.
Keywords: Brain metastasis; Non-small cell lung cancer; Prognosis; Treatment; epidermal growth factor receptor mutation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of EGFR-TKIs combined with intracranial radiotherapy in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases: a retrospective multi-institutional analysis.Radiat Oncol. 2025 Jan 9;20(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s13014-024-02578-4. Radiat Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39789554 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world utilization of EGFR TKIs and prognostic factors for survival in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases.Int J Cancer. 2021 Sep 1;149(5):1121-1128. doi: 10.1002/ijc.33677. Epub 2021 May 24. Int J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33970485
-
A comparative analysis of EGFR mutation status in association with the efficacy of TKI in combination with WBRT/SRS/surgery plus chemotherapy in brain metastasis from non-small cell lung cancer.J Neurooncol. 2014 Nov;120(2):423-30. doi: 10.1007/s11060-014-1570-7. Epub 2014 Aug 7. J Neurooncol. 2014. PMID: 25098700 Free PMC article.
-
First-line treatment with TKI plus brain radiotherapy versus TKI alone in EGFR-mutated non-small cell Lung cancer with brain metastases: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2023 Oct 30;23(1):1043. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11548-0. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37904083 Free PMC article.
-
Erlotinib as a salvage treatment after gefitinib failure for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients with brain metastasis: A successful case report and review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Jun 25;100(25):e26450. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000026450. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 34160440 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Afatinib in Untreated Stage IIIB/IV Lung Adenocarcinoma with Major Uncommon Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Mutations (G719X/L861Q/S768I): A Multicenter Observational Study in Taiwan.Target Oncol. 2023 Mar;18(2):195-207. doi: 10.1007/s11523-023-00946-w. Epub 2023 Feb 20. Target Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36805452 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Management of Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Brain Metastases, and Actionable Genomic Alterations: A Systematic Literature Review.Adv Ther. 2024 May;41(5):1815-1842. doi: 10.1007/s12325-024-02799-9. Epub 2024 Mar 21. Adv Ther. 2024. PMID: 38509433 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress on the Regulation Mechanism of Key Signal Pathways Affecting the Prognosis of Glioma.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Jul 22;15:910543. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.910543. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35935338 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69:7–34. - PubMed
-
- NCCN . Clinical practice guidelines in oncology (NCCN guidelines). Non-small cell lung Cancer. Version 4.2019. Fort Washington: National Comprehensive Cancer Network; 2019.
-
- Novello S, Barlesi F, Califano R, Cufer T, Ekman S, Levra MG, et al. Metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2016;27:v1–v27. - PubMed
-
- Soria JC, Ohe Y, Vansteenkiste J, Reungwetwattana T, Chewaskulyong B, Lee KH, et al. Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:113–125. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

