Pediatric otogenic cerebral venous sinus thrombosis: a case report and a literature review
- PMID: 32883359
- PMCID: PMC7470606
- DOI: 10.1186/s13052-020-00882-9
Pediatric otogenic cerebral venous sinus thrombosis: a case report and a literature review
Abstract
Background: Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis in children is a rare but potentially fatal complication of acute mastoiditis, one of the most common pediatric infectious diseases. Due to its subtle clinical presentation, suspicion is essential for a prompt diagnosis and appropriate management. Unfortunately, no standard treatment options are available. To discuss the possible clinical presentation, microbiology, and management, we here report the case of a child with otogenic cerebral venous sinus thrombosis and perform a literature review starting from 2011.
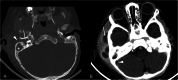
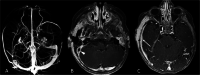
Case presentation: The child, a 10-months-old male, presented clinical signs of right acute otitis media and mastoiditis. Brain computed tomography scan detected right sigmoid and transverse sinus thrombosis, as well as a subperiosteal abscess. Fusobacterium necrophorum and Haemophilus Influentiae were detected on cultural sampling. A multidisciplinary approach along with a combination of medical and surgical therapy allowed the patient's full recovery.
Conclusion: Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis is a rare but severe complication of acute otitis media and mastoiditis. The management of this pathological condition is always challenging and an interdisciplinary approach is frequently required. Current therapeutic options include a combination of medical and surgical therapy. A patient-centered approach should guide timing and treatment management.
Keywords: Acute mastoiditis; Acute otitis media; Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis; Children; Fusobacterium necrophorum.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Castellazzi ML, Senatore L, Di Pietro G, Pinzani R, Torretta S, Coro I, Russillo A, Borzani I, Bosis S, Marchisio P. Otogenic temporomandibular septic arthritis in a child: a case report and a review of the literature. Ital J Pediatr. 2019;45(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s13052-019-0682-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- deVeber G, Andrew M, Adams C, Bjornson B, Booth F, Buckley DJ, Camfield CS, David M, Humphreys P, Langevin P, MacDonald EA, Gillett J, Meaney B, Shevell M, Sinclair DB, Yager J, Canadian Pediatric Ischemic Stroke Study Group Cerebral sinovenous thrombosis in children. N Engl J Med. 2001;345(6):417–423. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200108093450604. - DOI - PubMed

