CHD7 and Runx1 interaction provides a braking mechanism for hematopoietic differentiation
- PMID: 32883883
- PMCID: PMC7519295
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2003228117
CHD7 and Runx1 interaction provides a braking mechanism for hematopoietic differentiation
Erratum in
-
Correction for Hsu et al., CHD7 and Runx1 interaction provides a braking mechanism for hematopoietic differentiation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Sep 28;118(39):e2114827118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2114827118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34544883 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
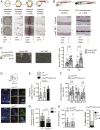
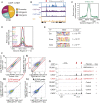
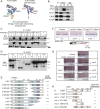
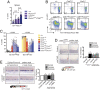
Hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell (HSPC) formation and lineage differentiation involve gene expression programs orchestrated by transcription factors and epigenetic regulators. Genetic disruption of the chromatin remodeler chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein 7 (CHD7) expanded phenotypic HSPCs, erythroid, and myeloid lineages in zebrafish and mouse embryos. CHD7 acts to suppress hematopoietic differentiation. Binding motifs for RUNX and other hematopoietic transcription factors are enriched at sites occupied by CHD7, and decreased RUNX1 occupancy correlated with loss of CHD7 localization. CHD7 physically interacts with RUNX1 and suppresses RUNX1-induced expansion of HSPCs during development through modulation of RUNX1 activity. Consequently, the RUNX1:CHD7 axis provides proper timing and function of HSPCs as they emerge during hematopoietic development or mature in adults, representing a distinct and evolutionarily conserved control mechanism to ensure accurate hematopoietic lineage differentiation.
Keywords: CHD7; RUNX1; hematopoiesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest statement: L.I.Z. is founder and stockholder of Fate, Scholar Rock, and Camp4 therapeutics and a scientific advisor for Stemgent.
Figures

References
-
- Sims J. K., Wade P. A., SnapShot: Chromatin remodeling: CHD. Cell 144, 626–626.e621 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 HL100405/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL144780/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL091724/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK049216/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL032262/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK092760/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 DK120535/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL089969/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_12009/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- T32 HL007439/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R24 OD017870/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 CA228135/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 12765/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- K12 CA076931/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C1163/A12765/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 HL095675/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK127738/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 097922/Z/11/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 21762/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- P01 HL131477/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 HL133828/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG002668/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK053298/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R00 CA148963/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

