Biocompatibility, Cytotoxicity, Antimicrobial and Epigenetic Effects of Novel Chitosan-Based Quercetin Nanohydrogel in Human Cancer Cells
- PMID: 32884259
- PMCID: PMC7441583
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S263013
Biocompatibility, Cytotoxicity, Antimicrobial and Epigenetic Effects of Novel Chitosan-Based Quercetin Nanohydrogel in Human Cancer Cells
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have reported that quercetin (Q) has a potential antibacterial and anticancer activity. However, its application is limited by many important factors including high hydrophobicity and low absorption.
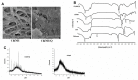
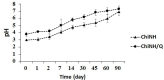
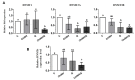
Methodology: In the current study, we synthesized and characterized (Patent) a novel chitosan-based quercetin nanohydrogel (ChiNH/Q). Encapsulation efficiency was confirmed by UV/VIS spectrophotometer. Physicochemical characterization of ChiNH/Q was assessed by PDI, DLS, SEM, FTIR, and XRD. The toxicity of the ChiNH/Q against five strains of the pathogen and HepG2 cells was examined. Moreover, the quantification of ChiNH/Q on genomic global DNA methylation and expression of DNMTs (DNMT1/3A/3B) in HepG2 cancer cells were evaluated by ELISA and real-time PCR, respectively.
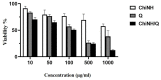
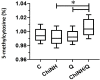
Results: Under the SEM-based images, the hydrodynamic size of the ChiNH/Q was 743.6 nm. The changes in the PDI were 0.507, and zeta potential was obtained as 12.1 mV for ChiNH/Q. The FTIR peak of ChiNH/Q showed the peak at 627 cm-1 corresponded to tensile vibrational of NH2-groups related to Q, and it is the indication of Q loading in the formulation. Moreover, XRD data have detected the encapsulation of ChiNH/Q. The ChiNH/Q showed a potent antimicrobial inhibitory effect and exerted cytotoxic effects against HepG2 cancer cells with IC50 values of 100 µg/mL. Moreover, our data have shown that ChiNH/Q effectively reduced (65%) the average expression level of all the three DNMTs (p<0.05) and significantly increased (1.01%) the 5-methylated cytosine (5-mC) levels in HepG2 cells.
Conclusion: Our results showed for the first time the bioavailability and potentiality of ChiNH/Q as a potent antimicrobial and anticancer agent against cancer cells. Our result provided evidence that ChiNH/Q could effectively reduce cellular DNMT expression levels and increase genomic global DNA methylation in HepG2 cancer cells. Our results suggest a potential clinical application of nanoparticles as antimicrobial and anticancer agents in combination cancer therapy.
Keywords: DNA methylation; antimicrobial activity; chitosan nanohydrogel; cytotoxic activity; gene expression; quercetin.
© 2020 Abbaszadeh et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Abd-Rabou AA, Shalby AB, Ahmed HH. Anti-cancer activity of quercetin, gallic acid, and ellagic acid against HEPG2 and HCT 116 cell lines: in vitro. Int J Pharm Biol Sci. 2016;4(5):B584–B592. doi:10.22376/ijpbs.2016.7.4.b584-592 - DOI
-
- Naghdi N. Folklore medicinal plants used in liver disease: a review. Int J Green Pharm. 2018;12(03).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

