Association Between Vitamin D Receptor Gene Polymorphism rs2228570 and Allergic Rhinitis
- PMID: 32884328
- PMCID: PMC7443006
- DOI: 10.2147/PGPM.S262402
Association Between Vitamin D Receptor Gene Polymorphism rs2228570 and Allergic Rhinitis
Abstract
Background: Vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene polymorphisms are involved in a variety of immune-related diseases, and VDR is associated with allergic rhinitis. The present study explored the associations between VDR gene polymorphisms and allergic rhinitis in the Chinese population.
Methods: The study population consisted of 400 patients with allergic rhinitis and 400 healthy controls. General characteristics were determined by interview. Blood DNA was extracted and genotyping was performed via matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. The associations of each genetic variant with risk for AR were assessed by calculating the odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence interval (95% CI).
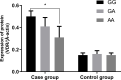
Results: No significant differences were observed in general characteristics between cases and controls. The distributions of genotypes at the rs2228570 locus of the VDR gene conformed to Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. There was a significant difference in the distribution of rs2228570 genotype (P<0.001) between cases and controls. Compared to GG and GA genotypes, the AA genotype increased the risk of AR (OR=3.27, 95% CI: 2.10-5.11, P=0.000; OR=2.58, 95% CI:1.63-4.08, P<0.001). Similar results were also observed in the dominant model (OR=1.64, 95% CI:1.24-2.17, P<0.001) and codominant model (OR=2.95, 95% CI:1.93-4.51, P<0.001). The A allele was still associated with elevated risk gene for AR after adjusting for potential confounding factors. Subgroup analyses indicated an interaction between alcohol and rs2228570 in the risk of allergic rhinitis. The A allele also increased the risk for AR in the population without asthma (OR=1.85, 95% CI:1.46-2.34, P<0.001).
Conclusion: VDR gene polymorphism is associated with AR, and the AA genotype of rs2228570 is associated with the increased risk of AR in the Chinese population.
Keywords: allergic rhinitis; case–control; gene polymorphism; vitamin D receptor.
© 2020 Zhang and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of vitamin D levels and VDR variant (rs2228570) with allergic rhinitis: A meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis.Heliyon. 2023 Jun 14;9(6):e17283. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17283. eCollection 2023 Jun. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37426797 Free PMC article.
-
[Analysis on correlation between single nucleotide polymorphisms of vitamin D receptor gene with susceptibility to allergic rhinitis].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019 May;33(5):402-406. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2019.05.005. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31163545 Chinese.
-
The Assessment of TNF-α Gene Polymorphism Association with the Risk of Allergic Rhinitis in the Chinese Han Population.Int J Gen Med. 2021 Sep 3;14:5183-5192. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S325969. eCollection 2021. Int J Gen Med. 2021. PMID: 34512001 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid-Induced Transcript 1(GLCCI1) SNP rs37937 Is Associated With the Risk of Developing Allergic Rhinitis and the Response to Intranasal Corticosteroids in a Chinese Han Population.Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2023 Nov;37(6):751-757. doi: 10.1177/19458924231193156. Epub 2023 Aug 8. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2023. PMID: 37553950
-
Frequency of rs731236 (Taql), rs2228570 (Fok1) of Vitamin-D Receptor (VDR) gene in Emirati healthy population.Meta Gene. 2015 Sep 15;6:49-52. doi: 10.1016/j.mgene.2015.09.001. eCollection 2015 Dec. Meta Gene. 2015. PMID: 26504744 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Association of Vitamin D Receptor Gene Polymorphisms with Vitamin D, Total IgE, and Blood Eosinophils in Patients with Atopy.Biomolecules. 2024 Feb 11;14(2):212. doi: 10.3390/biom14020212. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38397449 Free PMC article.
-
Association of vitamin D levels and VDR variant (rs2228570) with allergic rhinitis: A meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis.Heliyon. 2023 Jun 14;9(6):e17283. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17283. eCollection 2023 Jun. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37426797 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D receptor and vitamin D binding protein gene polymorphisms in patients with asthma: a pilot study.BMC Pulm Med. 2023 Jul 5;23(1):245. doi: 10.1186/s12890-023-02531-3. BMC Pulm Med. 2023. PMID: 37407930 Free PMC article.
-
CLEC16A variants conferred a decreased risk to allergic rhinitis in the Chinese population.Front Genet. 2022 Dec 12;13:1053761. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1053761. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36588789 Free PMC article.
-
Association of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism with type 1 diabetes mellitus risk in children: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Jul 16;100(28):e26637. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000026637. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 34260558 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials