May Measurement Month 2018: an analysis of blood pressure screening campaign results from Poland
- PMID: 32884486
- PMCID: PMC7455275
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/suaa041
May Measurement Month 2018: an analysis of blood pressure screening campaign results from Poland
Abstract
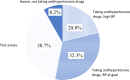
Hypertension remains the most important cardiovascular risk factor in Poland. May Measurement Month is a global initiative organized by the International Society of Hypertension aimed at raising awareness of hypertension and the need for blood pressure (BP) screening and demonstrating the potential of the opportunistic BP measurements. An opportunistic cross-sectional survey of volunteers aged ≥18 was carried out in 146 sites in May 2018. Blood pressure was measured in 6450 subjects (mean age: 41 ± 15 years; 59% females). After multiple imputation, the age and sex standardized systolic and diastolic BP was 126.7/78.4 mmHg in the whole analysed group, 132.8/81.3 mmHg in subjects taking antihypertensive drugs, and 125.7/78.0 mmHg in those not taking any antihypertensive drugs. After multiple imputation, the proportions of subjects with high BP (systolic ≥140 mmHg or diastolic ≥90 mmHg or on treatment for raised BP) were 22.2% in the whole analysed group, 39.2% in subjects taking antihypertensive drugs, and 18.6% those not taking any antihypertensive drugs. Overall, hypertension was present in 32.8% of participants, among them 38.7% were not aware of the disease, 53.1% were taking antihypertensive drugs, and 32.3% had BP controlled to target (<140/90 mmHg). Blood pressure was increasing with increasing body mass index and alcohol intake. Smokers and project participants with diabetes had increased average BP. In conclusion, this project provides additional evidence for a considerable potential for further reduction of cardiovascular risk through improvement in detection and treatment of hypertension in Poland.
Keywords: Blood pressure; Control; Disease awareness; Hypertension; Screening; Treatment.
Published on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology. © The Author(s) 2020.
Figures
References
-
- Rozkrut D, Adach-Stankiewicz E, Bielak R, Weglowska M. Statistical Year Book of the Republic of Poland 2018. Warsaw: Statistics Poland; 2018.
-
- Niklas A, Flotyńska A, Puch-Walczak A, Polakowska M, Topór-Madry R, Polak M, Piotrowski W, Kwaśniewska M, Nadrowski P, Pająk A, Bielecki W, Kozakiewicz K, Drygas W, Zdrojewski T, Tykarski A; WOBASZ II investigators. Prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension in the adult Polish population—Multi-center National Population Health Examination Surveys—WOBASZ studies. Arch Med Sci 2018;14:H951–H961. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Poulter NR, Lackland DT.. May Measurement Month: a global blood pressure screening campaign. Lancet 2017;389:H1678–H1680. - PubMed
-
- Małyszko J, Mastej M, Banach M, Tykarski A, Narkiewicz K, Hoffman P, Jankowski P, Nowicki MP, Tomasik T, Windak A, Olszanecka A, Motyl A, Nowak D, Skowron Ł, Tomaszewski M, Beaney T, Xia X, Nillson P, Poulter NR, Jóźwiak J.. Do we know more about hypertension in Poland after the May Measurement Month 2017?—Europe. Eur Heart J Suppl 2019;21:HD97–HD100. - PMC - PubMed