Identification of miRNA signature associated with BMP2 and chemosensitivity of TMZ in glioblastoma stem-like cells
- PMID: 32884997
- PMCID: PMC7452549
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2019.09.002
Identification of miRNA signature associated with BMP2 and chemosensitivity of TMZ in glioblastoma stem-like cells
Abstract
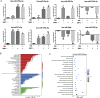
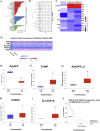
Glioblastoma multiform (GBM) is the most lethal intracranial tumor in adults. Glioblastoma stem-like cells (GSCs) are responsible for tumorigenesis and chemotherapy resistance. BMPs are known to increase temozolomide (TMZ) response in GSCs, however, the intracellular molecular mechanism remains largely unknown. In this study, we built a GSC cell model called U87S, and performed RNA sequencing to identify differentially expressed (DE) miRNA profiles in U87S cells treated with BMP2, TMZ or combined BMP2 and TMZ respectively. Bioinformatics analysis revealed that most DE miRNAs were involved in the cancer pathways, suggesting their crucial roles in gliomagenesis. Eight miRNAs from RNA-seq were validated. Four out of these miRNAs (has-miR-199a-3p, hsa-miR-374b-5p, hsa-miR-320d, and hsa-miR-339-5p) were found significantly up-regulated in GBM tumor tissues. One of them, hsa-miR-199a-3p, was significantly correlated with the survival of GBM patients, and differentially expressed in U87S cells. Expression of hsa-miR-199a-3p was up-regulated by BMP. Overexpression of hsa-miR-199a-3p in U87S cells inhibited cell viability and enhanced the cytotoxicity of TMZ. And activation of BMP boosted the effect of hsa-miR-199a-3p on cell viability and TMZ-mediated cytotoxicity. Besides, expressions of five predicted targets of hsa-miR-199a-3p were evaluated. Four of them were differentially expressed in GBM tumors. And one of them, SLC22A18, was associated with the survival of GBM patients. In the end, a hsa-miR-199a-3p-mediated ceRNA network was constructed for the convenience of future study. Together, our data provided DE miRNA expression profiles associated with BMP2 and TMZ in GSCs, which might lead to finding out miRNA-based target therapies that specially target GSCs.
Keywords: BMP2; Cancer stem cell; CeRNA; Gliobalstoma; RNA-seq; TMZ.
© 2019 Chongqing Medical University. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Figures




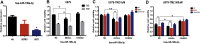

References
-
- Luo J.W., Wang X., Yang Y., Mao Q. Role of micro-RNA (miRNA) in pathogenesis of glioblastoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015;19(9):1630–1639. - PubMed
-
- Delgado-Lopez P.D., Corrales-Garcia E.M. Survival in glioblastoma: a review on the impact of treatment modalities. Clin Transl Oncol. 2016;18(11):1062–1071. - PubMed
-
- Filatova A., Acker T., Garvalov B.K. The cancer stem cell niche(s): the crosstalk between glioma stem cells and their microenvironment. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1830(2):2496–2508. - PubMed
-
- Qiang L., Yang Y., Ma Y.J. Isolation and characterization of cancer stem like cells in human glioblastoma cell lines. Cancer Lett. 2009;279(1):13–21. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

