Is it time to RE-AIM? A systematic review of economic empowerment as HIV prevention intervention for adolescent girls and young women in sub-Saharan Africa using the RE-AIM framework
- PMID: 32885209
- PMCID: PMC7427963
- DOI: 10.1186/s43058-020-00042-4
Is it time to RE-AIM? A systematic review of economic empowerment as HIV prevention intervention for adolescent girls and young women in sub-Saharan Africa using the RE-AIM framework
Abstract
Background: Economic empowerment (EE) HIV prevention programs for adolescent girls and young women (AGYW) in sub-Saharan Africa are gaining traction as effective strategies to reduce HIV risk and vulnerabilities among this population. While intervention effectiveness is critical, there are numerous factors beyond effectiveness that shape an intervention's impact. The objective of this systematic review was to assess the reporting of implementation outcomes of EE HIV prevention programs for AGYW in SSA, as conceptualized in the RE-AIM (reach, efficacy/effectiveness, adoption, implementation, and maintenance) framework.
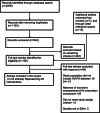
Methods: We searched PubMed, Ovid/MEDLINE, Science Direct, Ebscohost, PsycINFO, Scopus, and Web of Science for EE HIV interventions for AGYW in SSA. Study selection and data extraction were conducted according to the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses) guidelines. Two researchers coded each article using a validated RE-AIM data extraction tool and independently extracted information from each article. The reporting of RE-AIM dimensions were summarized and synthesized across included interventions.
Results: A total of 25 unique interventions (reported in 45 articles) met the predefined eligibility criteria. Efficacy/effectiveness 19(74.4%) was the highest reported RE-AIM dimension, followed by adoption 17(67.2%), reach 16(64.0%), implementation 9(38.0%), and maintenance 7(26.4%). Most interventions reported on RE-AIM components such as sample size 25(100.0%), intervention location 24(96.0%), and measures and results for at least one follow-up 24(96.0%). Few reported on RE-AIM components such as characteristics of non-participants 8(32.0%), implementation costs 3(12.0%), and intervention fidelity 0(0.0%).
Conclusions: Results of the review emphasize the need for future economic empowerment HIV prevention interventions for AGYW in SSA to report multiple implementation strategies and highlight considerations for translating such programs into real-world settings. Researchers should pay close attention to reporting setting-level adoption, implementation cost, and intervention maintenance. These measures are needed for policy decisions related to the full merit and worth of EE HIV interventions and their long-term sustainability for AGYW.
Keywords: Adolescent girls; Economic empowerment; RE-AIM; Sub-Saharan Africa; Young women.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests
Figures
Similar articles
-
A systematic review of randomized control trials of HPV self-collection studies among women in sub-Saharan Africa using the RE-AIM framework.Implement Sci Commun. 2021 Dec 15;2(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s43058-021-00243-5. Implement Sci Commun. 2021. PMID: 34911573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence and gap map report: Social and Behavior Change Communication (SBCC) interventions for strengthening HIV prevention and research among adolescent girls and young women (AGYW) in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs).Campbell Syst Rev. 2023 Jan 10;19(1):e1297. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1297. eCollection 2023 Mar. Campbell Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36911864 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
Music as an implementation strategy for evidence-based health interventions in Africa: a systematic review using the RE-AIM framework.Implement Sci Commun. 2025 May 30;6(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s43058-025-00741-w. Implement Sci Commun. 2025. PMID: 40448225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimising the implementation of digital-supported interventions for the secondary prevention of heart disease: a systematic review using the RE-AIM planning and evaluation framework.BMC Health Serv Res. 2023 Dec 4;23(1):1347. doi: 10.1186/s12913-023-10361-6. BMC Health Serv Res. 2023. PMID: 38049862 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Transactional sex and age-disparate sexual partnerships among adolescent girls and young women in Tanzania.Front Reprod Health. 2024 Jul 11;6:1360339. doi: 10.3389/frph.2024.1360339. eCollection 2024. Front Reprod Health. 2024. PMID: 39055125 Free PMC article.
-
Estimated contributions and future mitigation strategies for HIV risk around funeral practices in western Kenya: a mathematical modeling study.BMC Med. 2025 Feb 12;23(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s12916-025-03907-4. BMC Med. 2025. PMID: 39939974 Free PMC article.
-
Applying RE-AIM to evaluations of Veterans Health Administration Enterprise-Wide Initiatives: lessons learned.Front Health Serv. 2023 Jul 28;3:1209600. doi: 10.3389/frhs.2023.1209600. eCollection 2023. Front Health Serv. 2023. PMID: 37575975 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of educational intervention among seropositive women about knowledge about HIV sexual transmission.Rev Bras Enferm. 2023 Aug 21;76(3):e20220371. doi: 10.1590/0034-7167-2022-0371. eCollection 2023. Rev Bras Enferm. 2023. PMID: 37610951 Free PMC article.
-
Costs of implementing community-based intervention for HIV testing in sub-Saharan Africa: a systematic review.Implement Sci Commun. 2021 Jul 5;2(1):73. doi: 10.1186/s43058-021-00177-y. Implement Sci Commun. 2021. PMID: 34225820 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Women and HIV: A Spotlight on adolescent girls and young women [https://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/2019_women-and-hi...].
-
- UNAIDS: Women and HIV: spotlight on adolescent girls and young women. In. Geneva; 2019.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous