Serum response factor-cofactor interactions and their implications in disease
- PMID: 32885587
- PMCID: PMC7925694
- DOI: 10.1111/febs.15544
Serum response factor-cofactor interactions and their implications in disease
Abstract
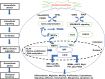
Serum response factor (SRF), a member of the Mcm1, Agamous, Deficiens, and SRF (MADS) box transcription factor, is widely expressed in all cell types and plays a crucial role in the physiological function and development of diseases. SRF regulates its downstream genes by binding to their CArG DNA box by interacting with various cofactors. However, the underlying mechanisms are not fully understood, therefore attracting increasing research attention due to the importance of this topic. This review's objective is to discuss the new progress in the studies of the molecular mechanisms involved in the activation of SRF and its impacts in physiological and pathological conditions. Notably, we summarized the recent studies on the interaction of SRF with its two main types of cofactors belonging to the myocardin families of transcription factors and the members of the ternary complex factors. The knowledge of these mechanisms will create new opportunities for understanding the dynamics of many traits and disease pathogenesis especially, cardiovascular diseases and cancer that could serve as targets for pharmacological control and treatment of these diseases.
Keywords: binding; cofactors; mechanisms; myocardin; serum response factor; transcription.
© 2020 The Authors. The FEBS Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Miano JM (2003) Serum response factor: toggling between disparate programs of gene expression. J Mol Cell Cardiol 35, 577–593. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

