Activation of cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway involved in therapeutic actions of α-mangostin on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats
- PMID: 32886564
- PMCID: PMC7485160
- DOI: 10.1177/2058738420954941
Activation of cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway involved in therapeutic actions of α-mangostin on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats
Abstract
Introduction: Alpha-mangostin (MAN) possesses a wide variety of pharmacological effects. In this study, we investigated its effect on cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway (CAP), and tested if CAP regulation was involved in the therapeutic action on acute lung injury (ALI).
Methods: Male Sprague Dawley rats were pre-treated with MAN (40 mg/kg) for 3 days and ALI was induced with an intraperitoneal injection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Certain rats received monolateral vagotomy or sham surgery. The effects on inflammatory reactions and relevant pathways in ALI rats or LPS pre-treated RAW 264.7 cells were investigated by histological, immunohistochemical, immunoblotting, RT-qPCR, and immunofluorescence assays, while levels of proinflammatory cytokines, acetylcholine (Ach) and the enzymatic activity of acetylcholinesterase (AchE) were determined by corresponding quantitative kits.
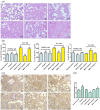
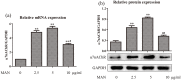
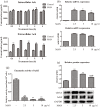
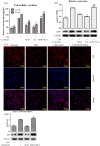
Results: Oral administration of MAN reduced the severity of ALI, while vagotomy surgery antagonized this effect. MAN restored the decline in α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (α7nAchR) in the lungs of ALI rats, and promoted the expression of α7nAchR and choline acetyltransferase (CHAT) in RAW 264.7 cells. Although AchE expression was barely affected by MAN at 5 μg/ml, its catalytic activity was reduced by almost 95%. Extracellular rather than intracellular Ach was notably raised shortly after MAN treatment. Furthermore, MAN at 5 μg/ml effectively inhibited LPS-induced increase in phosphorylation and nucleus translocation of p65 subunit, and secretion of TNF-α and IL-1β, which was then offset by methyllycaconitine citrate hydrate.
Conclusion: MAN activated CAP by increasing peripheral Ach and up-regulating α7nAchR expression, which eventually led to NF-κB inhibition and remission of acute inflammations.
Keywords: alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor; cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway; immunity; inflammation; α-mangostin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of Cholinergic Anti-Inflammatory Pathway in Peripheral Immune Cells Involved in Therapeutic Actions of α-Mangostin on Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Rats.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 May 22;14:1983-1993. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S249865. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 32546965 Free PMC article.
-
3-Dehydroandrographolide protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation through the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway.Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 Dec;158:305-317. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2018.10.034. Epub 2018 Nov 2. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30391477
-
Acute Lung Injury in Cholinergic-Deficient Mice Supports Anti-Inflammatory Role of α7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 14;22(14):7552. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147552. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34299169 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of α7nAChR-Mediated Cholinergic Anti-inflammatory Pathway in Immune Cells.Inflammation. 2021 Jun;44(3):821-834. doi: 10.1007/s10753-020-01396-6. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Inflammation. 2021. PMID: 33405021 Review.
-
Dual effects of supplemental oxygen on pulmonary infection, inflammatory lung injury, and neuromodulation in aging and COVID-19.Free Radic Biol Med. 2022 Sep;190:247-263. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.08.004. Epub 2022 Aug 11. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35964839 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway: an innovative strategy for treating diseases.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Feb 4;52(1):199. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10288-7. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39903351 Review.
-
Polyphenols from Securidaca inappendiculata alleviated acute lung injury in rats by inhibiting oxidative stress sensitive pathways.Chin Herb Med. 2021 Mar 2;13(3):381-388. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2020.09.007. eCollection 2021 Jul. Chin Herb Med. 2021. PMID: 36118931 Free PMC article.
-
The metabolic and molecular mechanisms of α‑mangostin in cardiometabolic disorders (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2022 Sep;50(3):120. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2022.5176. Epub 2022 Jul 29. Int J Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35904170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effects of Turmeric and Mangosteen Pericarp Ethanol Extract on Eosinophil Count, TNF-α and TGF-β1 Gene Expression in Asthmatic Rat Model.J Exp Pharmacol. 2024 Nov 1;16:397-411. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S471113. eCollection 2024. J Exp Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39502830 Free PMC article.
-
α-Mangostin Inhibited M1 Polarization of Macrophages/Monocytes in Antigen-Induced Arthritis Mice by Up-Regulating Silent Information Regulator 1 and Peroxisome Proliferators-Activated Receptor γ Simultaneously.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023 Feb 23;17:563-577. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S397914. eCollection 2023. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023. PMID: 36860800 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pedrazachaverri J, Cárdenasrodríguez N, Orozcoibarra M, et al. (2008) Medicinal properties of mangosteen ( Garcinia mangostana). Food and Chemical Toxicology 46: 3227–3239. - PubMed
-
- Chen G, Li Y, Wang W, et al. (2018) Bioactivity and pharmacological Properties of α-mangostin from the mangosteen fruit: A review. Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents 28: 13543776. - PubMed
-
- Yang K, Yin Q, Mao Q, et al. (2019) Metabolomics analysis reveals therapeutic effects of α-mangostin on collagen-induced arthritis in rats by down-regulating nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase. Inflammation 42: 741–753. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

