An Index for Lifting Social Distancing During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Algorithm Recommendation for Lifting Social Distancing
- PMID: 32886622
- PMCID: PMC7505695
- DOI: 10.2196/22469
An Index for Lifting Social Distancing During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Algorithm Recommendation for Lifting Social Distancing
Abstract
Background: Implementing and lifting social distancing (LSD) is an urgent global issue during the COVID-19 pandemic, particularly when the travel ban is lifted to revive international businesses and economies. However, when and whether LSD can be considered is subject to the spread of SARS-CoV-2, the recovery rate, and the case-fatality rate. It is imperative to provide real-time assessment of three factors to guide LSD.
Objective: A simple LSD index was developed for health decision makers to do real-time assessment of COVID-19 at the global, country, region, and community level.
Methods: Data on the retrospective cohort of 186 countries with three factors were retrieved from a publicly available repository from January to early July. A simple index for guiding LSD was measured by the cumulative number of COVID-19 cases and recoveries, and the case-fatality rate was envisaged. If the LSD index was less than 1, LSD can be considered. The dynamic changes of the COVID-19 pandemic were evaluated to assess whether and when health decision makers allowed for LSD and when to reimplement social distancing after resurgences of the epidemic.
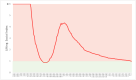
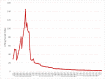
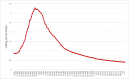
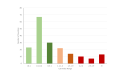
Results: After large-scale outbreaks in a few countries before mid-March (prepandemic phase), the global weekly LSD index peaked at 4.27 in March and lasted until mid-June (pandemic phase), during which most countries were affected and needed to take various social distancing measures. Since, the value of LSD has gradually declined to 0.99 on July 5 (postpandemic phase), at which 64.7% (120/186) of countries and regions had an LSD<1 with the decile between 0 and 1 to refine risk stratification by countries. The LSD index decreased to 1 in about 115 days. In addition, we present the results of dynamic changes of the LSD index for the world and for each country and region with different time windows from January to July 5. The results of the LSD index on the resurgence of the COVID-19 epidemic in certain regions and validation by other emerging infectious diseases are presented.
Conclusions: This simple LSD index provides a quantitative assessment of whether and when to ease or implement social distancing to provide advice for health decision makers and travelers.
Keywords: COVID-19; algorithm; data analysis; decision making; global health; index; pandemic; public health; social distancing.
©Sam Li-Sheng Chen, Amy Ming-Fang Yen, Chao-Chih Lai, Chen-Yang Hsu, Chang-Chuan Chan, Tony Hsiu-Hsi Chen. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (http://www.jmir.org), 17.09.2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of self-imposed prevention measures and short-term government-imposed social distancing on mitigating and delaying a COVID-19 epidemic: A modelling study.PLoS Med. 2020 Jul 21;17(7):e1003166. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003166. eCollection 2020 Jul. PLoS Med. 2020. PMID: 32692736 Free PMC article.
-
Willingness to Accept Trade-Offs Among COVID-19 Cases, Social-Distancing Restrictions, and Economic Impact: A Nationwide US Study.Value Health. 2020 Nov;23(11):1438-1443. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2020.07.003. Epub 2020 Sep 4. Value Health. 2020. PMID: 33127014 Free PMC article.
-
Could masks curtail the post-lockdown resurgence of COVID-19 in the US?Math Biosci. 2020 Nov;329:108452. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2020.108452. Epub 2020 Aug 18. Math Biosci. 2020. PMID: 32818515 Free PMC article.
-
Social distancing measures to control the COVID-19 pandemic: potential impacts and challenges in Brazil.Cien Saude Colet. 2020 Jun;25(suppl 1):2423-2446. doi: 10.1590/1413-81232020256.1.10502020. Epub 2020 Apr 22. Cien Saude Colet. 2020. PMID: 32520287 Review. English, Portuguese.
-
Role of modelling in COVID-19 policy development.Paediatr Respir Rev. 2020 Sep;35:57-60. doi: 10.1016/j.prrv.2020.06.013. Epub 2020 Jun 18. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2020. PMID: 32690354 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
New Surveillance Metrics for Alerting Community-Acquired Outbreaks of Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Variants Using Imported Case Data: Bayesian Markov Chain Monte Carlo Approach.JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2022 Nov 25;8(11):e40866. doi: 10.2196/40866. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2022. PMID: 36265134 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a social distancing monitoring system in Republic of Korea: results of a modified Delphi process.BMC Public Health. 2022 Apr 29;22(1):860. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-13277-8. BMC Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35488284 Free PMC article.
-
Modelling the impacts of COVID-19 pandemic on the quality of population-based colorectal cancer screening.Prev Med. 2021 Oct;151:106597. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2021.106597. Epub 2021 Jun 30. Prev Med. 2021. PMID: 34217416 Free PMC article.
-
Review of epidemic, containment strategies, clinical management, and economic evaluation of COVID-19 pandemic.J Formos Med Assoc. 2021 Jun;120 Suppl 1:S6-S18. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2021.05.022. Epub 2021 May 27. J Formos Med Assoc. 2021. PMID: 34116896 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nussbaumer-Streit B, Mayr V, Dobrescu AI, Chapman A, Persad E, Klerings I, Wagner G, Siebert U, Christof C, Zachariah C, Gartlehner G. Quarantine alone or in combination with other public health measures to control COVID‐19: a rapid review. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Apr 08;:CD013574. doi: 10.1002/14651858.cd013574. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kissler SM, Tedijanto C, Goldstein E, Grad YH, Lipsitch M. Projecting the transmission dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 through the postpandemic period. Science. 2020 May 22;368(6493):860–868. doi: 10.1126/science.abb5793. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/32291278 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chinazzi M, Davis JT, Ajelli M, Gioannini C, Litvinova M, Merler S, Pastore Y Piontti A, Mu K, Rossi L, Sun K, Viboud C, Xiong X, Yu H, Halloran ME, Longini IM, Vespignani A. The effect of travel restrictions on the spread of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak. Science. 2020 Apr 24;368(6489):395–400. doi: 10.1126/science.aba9757. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/32144116 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

