Dicke model
- PMID: 32886669
- PMCID: PMC7473565
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0235197
Dicke model
Abstract
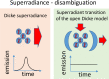
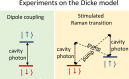
The Dicke model is a fundamental model of quantum optics, which describes the interaction between light and matter. In the Dicke model, the light component is described as a single quantum mode, while the matter is described as a set of two-level systems. When the coupling between the light and matter crosses a critical value, the Dicke model shows a mean-field phase transition to a superradiant phase. This transition belongs to the Ising universality class and was realized experimentally in cavity quantum electrodynamics experiments. Although the superradiant transition bears some analogy with the lasing instability, these two transitions belong to different universality classes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Hepp Klaus; Lieb Elliott H (1973). "On the superradiant phase transition for molecules in a quantized radiation field: the dicke maser model". Annals of Physics. 76 (2): 360–404. 10.1016/0003-4916(73)90039-0 ISSN 0003–4916. - DOI
-
- Dicke R. H. (1954). "Coherence in Spontaneous Radiation Processes". Physical Review. 93 (1): 99–110. 10.1103/PhysRev.93.99 ISSN 0031-899X. - DOI
-
- Larson Jonas; Irish Elinor K (2017). "Some remarks on 'superradiant' phase transitions in light-matter systems". Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and Theoretical. 50 (17): 174002 10.1088/1751-8121/aa65dc ISSN 1751–8113. - DOI
-
- Kirton Peter; Roses Mor M.; Keeling Jonathan; Dalla Torre Emanuele G. (2018). "Introduction to the Dicke Model: From Equilibrium to Nonequilibrium, and Vice Versa". Advanced Quantum Technologies: 1800043 10.1002/qute.201800043 ISSN 2511–9044. and references therein. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

