Phenotypical and functional alteration of unconventional T cells in severe COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 32886755
- PMCID: PMC7472174
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20200872
Phenotypical and functional alteration of unconventional T cells in severe COVID-19 patients
Abstract
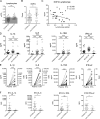
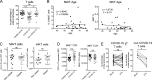
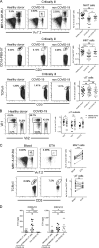
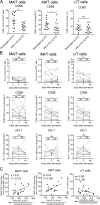
COVID-19 includes lung infection ranging from mild pneumonia to life-threatening acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Dysregulated host immune response in the lung is a key feature in ARDS pathophysiology. However, cellular actors involved in COVID-19-driven ARDS are poorly understood. Here, in blood and airways of severe COVID-19 patients, we serially analyzed unconventional T cells, a heterogeneous class of T lymphocytes (MAIT, γδT, and iNKT cells) with potent antimicrobial and regulatory functions. Circulating unconventional T cells of COVID-19 patients presented with a profound and persistent phenotypic alteration. In the airways, highly activated unconventional T cells were detected, suggesting a potential contribution in the regulation of local inflammation. Finally, expression of the CD69 activation marker on blood iNKT and MAIT cells of COVID-19 patients on admission was predictive of clinical course and disease severity. Thus, COVID-19 patients present with an altered unconventional T cell biology, and further investigations will be required to precisely assess their functions during SARS-CoV-2-driven ARDS.
© 2020 Jouan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: S. Ehrmann reported personal fees from Aerogen, grants from Fisher & Paykel, grants from Hamilton Medical, and personal fees from La Diffusion Technique Française outside the submitted work. M. Si-Tahar reported personal fees from Cynbiose Respiratory outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures




Comment in
-
An unconventional view of COVID-19 T cell immunity.J Exp Med. 2020 Dec 7;217(12):e20201727. doi: 10.1084/jem.20201727. J Exp Med. 2020. PMID: 33147321 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

