Ubiquitin, Autophagy and Neurodegenerative Diseases
- PMID: 32887381
- PMCID: PMC7563958
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9092022
Ubiquitin, Autophagy and Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
Ubiquitin signals play various roles in proteolytic and non-proteolytic functions. Ubiquitin signals are recognized as targets of the ubiquitin-proteasome system and the autophagy-lysosome pathway. In autophagy, ubiquitin signals are required for selective incorporation of cargoes, such as proteins, organelles, and microbial invaders, into autophagosomes. Autophagy receptors possessing an LC3-binding domain and a ubiquitin binding domain are involved in this process. Autophagy activity can decline as a result of genetic variation, aging, or lifestyle, resulting in the onset of various neurodegenerative diseases. This review summarizes the selective autophagy of neurodegenerative disease-associated protein aggregates via autophagy receptors and discusses its therapeutic application for neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: autophagy; autophagy–lysosome pathway; neurodegenerative diseases; ubiquitin; ubiquitin–proteasome system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
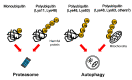

References
-
- Ziv I., Matiuhin Y., Kirkpatrick D.S., Erpapazoglou Z., Leon S., Pantazopoulou M., Kim W., Gygi S.P., Haguenauer-Tsapis R., Reis N., et al. A perturbed ubiquitin landscape distinguishes between ubiquitin in trafficking and in proteolysis. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2011;10:M111.009753. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M111.009753. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

