Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Cardiovascular Toxicity of Specific Uremic Solutes
- PMID: 32887404
- PMCID: PMC7565564
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9092024
Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Cardiovascular Toxicity of Specific Uremic Solutes
Abstract
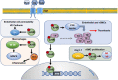
Mounting evidence strongly suggests a causal link between chronic kidney disease (CKD) and cardiovascular disease (CVD). Compared with non-CKD patients, patients with CKD suffer disproportionately from CVD and derive suboptimal benefits from interventions targeting conventional CVD risk factors. Uremic toxins (UTs), whose plasma levels rapidly rise as CKD progresses, represent a unique risk factor in CKD, which has protean manifestations on CVD. Among the known UTs, tryptophan metabolites and trimethylamine N-oxide are well-established cardiovascular toxins. Their molecular mechanisms of effect warrant special consideration to draw translational value. This review surveys current knowledge on the effects of specific UTs on different pathways and cell functions that influence the integrity of cardiovascular health, with implication for CVD progression. The effect of UTs on cardiovascular health is an example of a paradigm in which a cascade of molecular and metabolic events induced by pathology in one organ in turn induces dysfunction in another organ. Deciphering the molecular mechanisms underlying such cross-organ pathologies will help uncover therapeutic targets to improve the management of CVD in patients with CKD.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; chronic kidney disease; uremic toxins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor-activating effect of uremic toxins from tryptophan metabolism: a new concept to understand cardiovascular complications of chronic kidney disease.Toxins (Basel). 2014 Mar 4;6(3):934-49. doi: 10.3390/toxins6030934. Toxins (Basel). 2014. PMID: 24599232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Uraemic solutes as therapeutic targets in CKD-associated cardiovascular disease.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2021 Jun;17(6):402-416. doi: 10.1038/s41581-021-00408-4. Epub 2021 Mar 23. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33758363 Review.
-
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor and Uremic Toxins from the Gut Microbiota in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients: Is There a Relationship between Them?Biochemistry. 2019 Apr 16;58(15):2054-2060. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b01305. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Biochemistry. 2019. PMID: 30912928
-
Mechanisms of tissue factor induction by the uremic toxin indole-3 acetic acid through aryl hydrocarbon receptor/nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway in human endothelial cells.Arch Toxicol. 2019 Jan;93(1):121-136. doi: 10.1007/s00204-018-2328-3. Epub 2018 Oct 15. Arch Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 30324315
-
Role of Uremic Toxins for Kidney, Cardiovascular, and Bone Dysfunction.Toxins (Basel). 2018 May 16;10(5):202. doi: 10.3390/toxins10050202. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29772660 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Serum Orotidine: A Novel Biomarker of Increased CVD Risk in Type 2 Diabetes Discovered Through Metabolomics Studies.Diabetes Care. 2022 Aug 1;45(8):1882-1892. doi: 10.2337/dc21-1789. Diabetes Care. 2022. PMID: 35696261 Free PMC article.
-
Toxin Removal and Inflammatory State Modulation during Online Hemodiafiltration Using Two Different Dialyzers (TRIAD2 Study).Methods Protoc. 2021 Apr 22;4(2):26. doi: 10.3390/mps4020026. Methods Protoc. 2021. PMID: 33921921 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular Risk Comparison between Expanded Hemodialysis Using Theranova and Online Hemodiafiltration (CARTOON): A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial.Sci Rep. 2021 May 24;11(1):10807. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-90311-6. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34031503 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Uremic Toxins Induce THP-1 Monocyte Endothelial Adhesion and Migration through Specific miRNA Expression.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 18;24(16):12938. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612938. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37629118 Free PMC article.
-
New Strategies for the Reduction of Uremic Toxins: How Much More We Know.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Nov 24;13(12):837. doi: 10.3390/toxins13120837. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34941675 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Temgoua M.N., Danwang C., Agbor V.N., Noubiap J.J. Prevalence, incidence and associated mortality of cardiovascular disease in patients with chronic kidney disease in low- and middle-income countries: A protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2017;7:e016412. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-016412. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

