Ocular Adverse Effects of Infigratinib, a New Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor
- PMID: 32888946
- PMCID: PMC12079666
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2020.08.026
Ocular Adverse Effects of Infigratinib, a New Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor
Figures
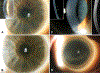
Comment in
-
Reply.Ophthalmology. 2021 Sep;128(9):e44-e45. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2021.05.015. Epub 2021 Jun 21. Ophthalmology. 2021. PMID: 34167829 No abstract available.
-
Re: Magone et al.: Ocular adverse effects of infigratinib, a new fibroblast growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor (Ophthalmology. 2021;128:624-626).Ophthalmology. 2021 Sep;128(9):e43-e44. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2021.05.012. Epub 2021 Jun 21. Ophthalmology. 2021. PMID: 34167830 No abstract available.
References
-
- Klenkler B, Sheardown H. Growth factors in the anterior segment: role in tissue maintenance, wound healing and ocular pathology. Exp Eye Res 2004;79:677–688. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

