Management of Osteomyelitis in Sickle Cell Disease: Review Article
- PMID: 32890008
- PMCID: PMC7470010
- DOI: 10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-20-00002
Management of Osteomyelitis in Sickle Cell Disease: Review Article
Abstract
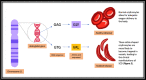
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is an autosomal recessive disorder that is characterized by abnormal "sickle-shaped" erythrocytes. Because of their shape, these erythrocytes are more likely to become trapped in small slow-flowing vessels, leading to vaso-occlusion. Because this commonly happens in the bones, patients with SCD are at an increased risk for orthopaedic manifestations such as osteomyelitis, septic joint, or osteonecrosis. Osteomyelitis is a serious and potentially disabling condition but can be difficult to differentiate from benign conditions of SCD, such as vaso-occlusive crisis. Diagnosis of osteomyelitis requires careful evaluation of the clinical presentation, laboratory testing, and imaging. Treatment of osteomyelitis in patients with SCD may be medical or surgical, but considerations in antibiotic selection and management preoperatively and postoperatively must be taken to ensure optimal outcomes.
Figures




References
-
- Ware RE, de Montalembert M, Tshilolo L, Abboud MR: Sickle cell disease. Lancet 2017;390:311-323. - PubMed
-
- Hassell K: Population estimates of sickle cell disease in the U.S. Am J Prev Med 2010;38:S512-S521. - PubMed
-
- Vanderhave K, Perkins C, Scannell B, Brighton B: Orthopaedic manifestations of sickle cell disease. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2018;26:94-101. - PubMed
-
- Berger E, Saunders N, Wang L, Friedman JN: Sickle cell disease in children: Differentiating osteomyelitis from vaso-occlusive crisis. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2009;163:251-255. - PubMed
-
- Rees DC, Williams TN, Gladwin MT: Sickle-cell disease. Lancet 2010;376:2018-2031. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

