Gait and balance disturbances are common in young urbanites and associated with cognitive impairment. Air pollution and the historical development of Alzheimer's disease in the young
- PMID: 32890478
- PMCID: PMC7467072
- DOI: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.110087
Gait and balance disturbances are common in young urbanites and associated with cognitive impairment. Air pollution and the historical development of Alzheimer's disease in the young
Abstract
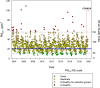
To determine whether gait and balance dysfunction are present in young urbanites exposed to fine particular matter PM2.5 ≥ annual USEPA standard, we tested gait and balance with Tinetti and Berg tests in 575 clinically healthy subjects, age 21.0 ± 5.7 y who were residents in Metropolitan Mexico City, Villahermosa and Reynosa. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment was also applied to an independent cohort n:76, age 23.3 ± 9.1 y. In the 575 cohort, 75.4% and 34.4% had abnormal total Tinetti and Berg scores and high risk of falls in 17.2% and 5.7% respectively. BMI impacted negatively Tinetti and Berg performance. Gait dysfunction worsen with age and males performed worse than females. Gait and balance dysfunction were associated with mild cognitive impairment MCI (19.73%) and dementia (55.26%) in 57/76 and 19 cognitively intact subjects had gait and balance dysfunction. Seventy-five percent of urbanites exposed to PM2.5 had gait and balance dysfunction. For MMC residents-with historical documented Alzheimer disease (AD) and CSF abnormalities, these findings suggest Alzheimer Continuum is in progress. Early development of a Motoric Cognitive Risk Syndrome ought to be considered in city dwellers with normal cognition and gait dysfunction. The AD research frame in PM2.5 exposed young urbanites should include gait and balance measurements. Multicity teens and young adult cohorts are warranted for quantitative gait and balance measurements and neuropsychological and brain imaging studies in high vs low PM2.5 exposures. Early identification of gait and balance impairment in young air pollution-exposed urbanites would facilitate multidisciplinary prevention efforts for modifying the course of AD.
Keywords: Air pollution; Alzheimer; Alzheimer continuum; Balance; Berg; Cognition; Dementia; Diesel; Gait; Mexico City; Mild cognitive impairment MCI; MoCA; Motoric cognitive risk syndrome MCR; Nanoparticles; PM (2.5); Tinetti; Young adults.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia Involving Multiple Cognitive Domains in Mexican Urbanites.J Alzheimers Dis. 2019;68(3):1113-1123. doi: 10.3233/JAD-181208. J Alzheimers Dis. 2019. PMID: 30909241
-
Alzheimer disease starts in childhood in polluted Metropolitan Mexico City. A major health crisis in progress.Environ Res. 2020 Apr;183:109137. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.109137. Epub 2020 Jan 25. Environ Res. 2020. PMID: 32006765 Review.
-
TDP-43 CSF Concentrations Increase Exponentially with Age in Metropolitan Mexico City Young Urbanites Highly Exposed to PM2.5 and Ultrafine Particles and Historically Showing Alzheimer and Parkinson's Hallmarks. Brain TDP-43 Pathology in MMC Residents Is Associated with High Cisternal CSF TDP-43 Concentrations.Toxics. 2022 Sep 24;10(10):559. doi: 10.3390/toxics10100559. Toxics. 2022. PMID: 36287840 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers in Highly Exposed PM2.5 Urbanites: The Risk of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Diseases in Young Mexico City Residents.J Alzheimers Dis. 2016 Sep 6;54(2):597-613. doi: 10.3233/JAD-160472. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016. PMID: 27567860
-
Apolipoprotein E4, Gender, Body Mass Index, Inflammation, Insulin Resistance, and Air Pollution Interactions: Recipe for Alzheimer's Disease Development in Mexico City Young Females.J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;58(3):613-630. doi: 10.3233/JAD-161299. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017. PMID: 28527212 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases, frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis overlapping neuropathology start in the first two decades of life in pollution exposed urbanites and brain ultrafine particulate matter and industrial nanoparticles, including Fe, Ti, Al, V, Ni, Hg, Co, Cu, Zn, Ag, Pt, Ce, La, Pr and W are key players. Metropolitan Mexico City health crisis is in progress.Front Hum Neurosci. 2024 Jan 12;17:1297467. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2023.1297467. eCollection 2023. Front Hum Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38283093 Free PMC article.
-
Environmentally Toxic Solid Nanoparticles in Noradrenergic and Dopaminergic Nuclei and Cerebellum of Metropolitan Mexico City Children and Young Adults with Neural Quadruple Misfolded Protein Pathologies and High Exposures to Nano Particulate Matter.Toxics. 2022 Mar 29;10(4):164. doi: 10.3390/toxics10040164. Toxics. 2022. PMID: 35448425 Free PMC article.
-
Scientometric Research and Critical Analysis of Gait and Balance in Older Adults.Sensors (Basel). 2024 May 17;24(10):3199. doi: 10.3390/s24103199. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38794055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sleep matters: Neurodegeneration spectrum heterogeneity, combustion and friction ultrafine particles, industrial nanoparticle pollution, and sleep disorders-Denial is not an option.Front Neurol. 2023 Feb 27;14:1117695. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1117695. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36923490 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A perspective on persistent toxicants in veterans and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: identifying exposures determining higher ALS risk.J Neurol. 2022 May;269(5):2359-2377. doi: 10.1007/s00415-021-10928-5. Epub 2022 Jan 1. J Neurol. 2022. PMID: 34973105 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

